Dual effects of insulin resistance on mortality and function in non-diabetic older adults: findings from the Toledo Study of Healthy Aging
- PMID: 34075557
- PMCID: PMC9135930
- DOI: 10.1007/s11357-021-00384-4
Dual effects of insulin resistance on mortality and function in non-diabetic older adults: findings from the Toledo Study of Healthy Aging
Abstract
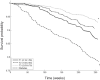
Insulin signalling declines with increasing age and impacts skeletal muscle function and longevity in animal models. Our aim was to assess the relationships between insulin resistance (IR) and frailty and mortality in a unique community-dwelling cohort of older people. 991 non-diabetic subjects from the Toledo Study of Healthy Ageing (TSHA) cohort were included. IR was estimated by the homeostasis model assessment index (HOMA-IR) at baseline while frailty was determined by frailty phenotype (FP) and Frailty Trait Scale (FTS) at baseline and after 5-year follow-up. Deaths were also determined. Multivariate regression models were used to analyze the effects of HOMA-IR on outcomes. Age, gender, BMI, education level, cardio- and cerebro-vascular disease, glomerular filtration rate, and disability were included as potential confounding variables in progressive adjustment models. IR determined as increasing log HOMA-IR was inversely associated with risk of mortality. The association remained significant for all adjustment models (HR: 0.64-0.69). When we analyzed survival curves, the higher the HOMA-IR tertile, the lower the mortality rate (highest vs lowest tertile, p = 0.0082). In contrast, IR increased the risk of incident frailty determined by FP (OR 1.81 [1.14-2.87]) as well as deterioration of frailty status determined by worsening in FTS score (OR 1.28 [1.01-1.63]) at 5-year follow-up. In non-diabetic older subjects, IR significantly increases the risk for frailty and functional decline but decreased the risk of death at 5-year follow-up. This finding raises the need of assessing the effect of biomarkers on different outcomes before establishing their role as biomarkers of aging.
Keywords: Aging; Frailty; Functional performance; Insulin resistance; Mortality.
© 2021. American Aging Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fat Mass Accounts for Insulin Resistance Impact on Functional Decline and Mortality in Nondiabetic Older Adults.J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2024 Mar;25(3):448-453. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2023.09.015. Epub 2023 Oct 25. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2024. PMID: 37898163
-
Gender-specific capacity of insulin resistance proxies to predict functional decline in older adults.J Nutr Health Aging. 2024 Nov;28(11):100376. doi: 10.1016/j.jnha.2024.100376. Epub 2024 Sep 23. J Nutr Health Aging. 2024. PMID: 39316897
-
Associations between frailty trajectories and frailty status and adverse outcomes in community-dwelling older adults.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022 Feb;13(1):230-239. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12888. Epub 2021 Dec 23. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022. PMID: 34951157 Free PMC article.
-
Is there a relationship between insulin resistance and frailty syndrome?Curr Pharm Des. 2008;14(4):405-10. doi: 10.2174/138161208783497750. Curr Pharm Des. 2008. PMID: 18289066 Review.
-
Predictive Value of Insulin Resistance as Determined by Homeostasis Model Assessment in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Horm Metab Res. 2021 Nov;53(11):746-751. doi: 10.1055/a-1648-7767. Epub 2021 Nov 5. Horm Metab Res. 2021. PMID: 34740276
Cited by
-
Effect of dietary protein content shift on aging in elderly rats by comprehensive quantitative score and metabolomics analysis.Front Nutr. 2022 Nov 3;9:1051964. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1051964. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36407526 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Syndrome and Positive Frailty Screening: A Cross-Sectional Study with Community-Dwelling Older Adults.JAR Life. 2024 May 27;13:82-87. doi: 10.14283/jarlife.2024.12. eCollection 2024. JAR Life. 2024. PMID: 38817671 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbial DNA and immune checkpoint gene Vsig4/CRIg are key antagonistic players in healthy aging and age-associated development of hypertension and diabetes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 11;13:1037465. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1037465. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36440192 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of surrogates for insulin resistance on mortality and life expectancy in primary care: a nationwide cross-sectional study with registry linkage (LIPIDOGRAM2015).Lancet Reg Health Eur. 2024 Dec 12;49:101182. doi: 10.1016/j.lanepe.2024.101182. eCollection 2025 Feb. Lancet Reg Health Eur. 2024. PMID: 39759579 Free PMC article.
-
Course and trajectories of insulin resistance, incident heart failure and all-cause mortality in nondiabetic people.Endocrine. 2025 Feb;87(2):530-542. doi: 10.1007/s12020-024-04037-2. Epub 2024 Sep 18. Endocrine. 2025. PMID: 39292366
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

