A quinazoline-based bromodomain inhibitor, CN210, ameliorates indomethacin-induced ileitis in mice by inhibiting inflammatory cytokine expression
- PMID: 34075610
- PMCID: PMC8637501
- DOI: 10.1002/ddr.21838
A quinazoline-based bromodomain inhibitor, CN210, ameliorates indomethacin-induced ileitis in mice by inhibiting inflammatory cytokine expression
Abstract
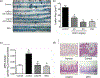
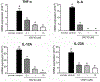
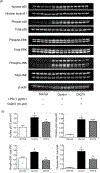
Inhibitors of bromodomain and extra-terminal motif (BET) proteins are emerging epigenetic therapeutics that suppress gene expressions that drive cancer and inflammation. The present study examined anti-inflammatory effects of a quinazoline-based BET inhibitor, CN210, in a murine ileitis model. CN210 was given orally 30 min before and 24 h after a subcutaneous administration of indomethacin. Macroscopic and histological evidences of ileitis, mucosal myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity and cytokine expressions were evaluated 48 h after the indomethacin administration. To further characterize the anti-inflammatory pathways modulated by CN210, its effects on RAW264 cells treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) were investigated. Competitive ligand binding and docking studies of CN210 to CREB-binding protein (CBP) and p300 were also performed. Oral administration of CN210 significantly reduced the severity of ileitis, normalized both proinflammatory MPO activity and concomitant cytokine expressions induced by indomethacin administration. Furthermore, CN210 attenuated the expression of cytokines and reversed the activation of nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) induced by LPS. Competitive ligand binding assays showed that CN210 bound to the bromodomains of two paralogous histone acetyltransferases, CBP and p300, in addition to the bromodomains of BET proteins. Docking studies of CN210 to the bromodomains of CBP and p300 showed a similarity to the binding mode of SGC-CBP30, a specific CBP/p300 inhibitor. CN210 ameliorates indomethacin-induced ileitis by inhibiting the expression of inflammatory cytokines through the attenuation of NF-κB and MAPK pathways. CN210 thus represents a new mode of therapy for non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced ileitis and inflammatory bowel disease.
Keywords: CREB-binding protein (CBP) and p300; bromodomain and extra-terminal motif (BET) proteins; ileitis.
© 2021 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare the following competing financial interests: Makoto Yoshioka is employed by ConverGene LLC and holds equity in ConverGene LLC.
Figures
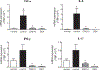

Similar articles
-
CN470 is a BET/CBP/p300 multi-bromodomain inhibitor and has an anti-tumor activity against MLL-rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022 Jan 29;590:49-54. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.12.078. Epub 2021 Dec 24. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022. PMID: 34971957 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the RelA:CBP/p300 interaction reveals its involvement in NF-κB-driven transcription.PLoS Biol. 2013 Sep;11(9):e1001647. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001647. Epub 2013 Sep 3. PLoS Biol. 2013. PMID: 24019758 Free PMC article.
-
PNSC5325 prevents acute respiratory distress syndrome by alleviating inflammation and inhibiting extracellular matrix degradation of alveolar macrophages.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Dec 25;143(Pt 3):113579. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113579. Epub 2024 Nov 8. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39520964
-
Classical molecular dynamics and metadynamics simulations decipher the mechanism of CBP30 selectively inhibiting CBP/p300 bromodomains.Org Biomol Chem. 2018 Sep 11;16(35):6521-6530. doi: 10.1039/c8ob01526k. Org Biomol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30160288
-
The important role of the histone acetyltransferases p300/CBP in cancer and the promising anticancer effects of p300/CBP inhibitors.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2025 Jan 17;41(1):32. doi: 10.1007/s10565-024-09984-0. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39825161 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetics of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases.Turk J Gastroenterol. 2023 May;34(5):437-448. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2023.22515. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37158530 Free PMC article.
-
E prostanoid receptor-3 promotes oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced human aortic smooth muscle cells inflammation.ESC Heart Fail. 2023 Apr;10(2):1077-1089. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14264. Epub 2022 Dec 28. ESC Heart Fail. 2023. PMID: 36578105 Free PMC article.
-
NSAID-Associated Small Intestinal Injury: An Overview From Animal Model Development to Pathogenesis, Treatment, and Prevention.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Feb 9;13:818877. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.818877. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35222032 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anthony A, Pounder RE, Dhillon AP, & Wakefield AJ (2000). Similarities between ileal Crohn’s disease and indomethacin experimental jejunal ulcers in the rat. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 14, 241–245. - PubMed
-
- Bandukwala HS, Gagnon J, Togher S, Greenbaum JA, Lamperti ED, Parr NJ, Molesworth AM, Smithers N, Lee K, Witherington J, Tough DF, Prinjha RK, Peters B, & Rao A. (2012). Selective inhibition of CD4+ T-cell cytokine production and autoimmunity by BET protein and c-Myc inhibitors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109, 14532–14537. 10.1073/pnas.1212264109 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brown JD, Lin CY, Duan Q, Griffin G, Federation A, Paranal RM, Bair S, Newton G, Lichtman A, Kung A, Yang T, Wang H, Luscinskas FW, Croce K, Bradner JE, & Plutzky J. (2014). NFkappaB directs dynamic super enhancer formation in inflammation and atherogenesis. Molecular Cell, 56, 219–231. 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.08.024 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

