Characterization of an aminotransferase from Acanthamoeba polyphaga Mimivirus
- PMID: 34076307
- PMCID: PMC8376416
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.4139
Characterization of an aminotransferase from Acanthamoeba polyphaga Mimivirus
Abstract
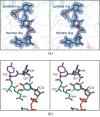
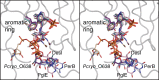
Acanthamoeba polyphaga Mimivirus, a complex virus that infects amoeba, was first reported in 2003. It is now known that its DNA genome encodes for nearly 1,000 proteins including enzymes that are required for the biosynthesis of the unusual sugar 4-amino-4,6-dideoxy-d-glucose, also known as d-viosamine. As observed in some bacteria, the pathway for the production of this sugar initiates with a nucleotide-linked sugar, which in the Mimivirus is thought to be UDP-d-glucose. The enzyme required for the installment of the amino group at the C-4' position of the pyranosyl moiety is encoded in the Mimivirus by the L136 gene. Here, we describe a structural and functional analysis of this pyridoxal 5'-phosphate-dependent enzyme, referred to as L136. For this analysis, three high-resolution X-ray structures were determined: the wildtype enzyme/pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate/dTDP complex and the site-directed mutant variant K185A in the presence of either UDP-4-amino-4,6-dideoxy-d-glucose or dTDP-4-amino-4,6-dideoxy-d-glucose. Additionally, the kinetic parameters of the enzyme utilizing either UDP-d-glucose or dTDP-d-glucose were measured and demonstrated that L136 is efficient with both substrates. This is in sharp contrast to the structurally related DesI from Streptomyces venezuelae, whose three-dimensional architecture was previously reported by this laboratory. As determined in this investigation, DesI shows a profound preference in its catalytic efficiency for the dTDP-linked sugar substrate. This difference can be explained in part by a hydrophobic patch in DesI that is missing in L136. Notably, the structure of L136 reported here represents the first three-dimensional model for a virally encoded PLP-dependent enzyme and thus provides new information on sugar aminotransferases in general.
Keywords: d-viosamine; 4,6-dideoxy sugar; 4-aminoquinovose; Acanthamoeba polyphaga Mimivirus; UDP-4-amino-4,6-dideoxy-d-glucose; X-ray structure; aminotransferase; giant viruses; viral glycans.
© 2021 The Protein Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing financial interests.
Figures








References
-
- Bos L. The embryonic beginning of virology: Unbiased thinking and dogmatic stagnation. Arch Virol. 1995;140:613–619. - PubMed
-
- La Scola B, Audic S, Robert C, et al. A giant virus in amoebae. Science. 2003;299:2033. - PubMed
-
- Xiao C, Chipman PR, Battisti AJ, et al. Cryo‐electron microscopy of the giant Mimivirus . J Mol Biol. 2005;353:493–496. - PubMed
-
- Raoult D, Audic S, Robert C, et al. The 1.2‐megabase genome sequence of Mimivirus . Science. 2004;306:1344–1350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

