Ending a diagnostic odyssey: Moving from exome to genome to identify cockayne syndrome
- PMID: 34076366
- PMCID: PMC8372079
- DOI: 10.1002/mgg3.1623
Ending a diagnostic odyssey: Moving from exome to genome to identify cockayne syndrome
Abstract
Background: Cockayne syndrome (CS) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by growth failure and multisystemic degeneration. Excision repair cross-complementation group 6 (ERCC6 OMIM: *609413) is the gene most frequently mutated in CS.
Methods: A child with pre and postnatal growth failure and progressive neurologic deterioration with multisystem involvement, and with nondiagnostic whole-exome sequencing, was screened for causal variants with whole-genome sequencing (WGS).
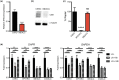
Results: WGS identified biallelic ERCC6 variants, including a previously unreported intronic variant. Pathogenicity of these variants was established by demonstrating reduced levels of ERCC6 mRNA and protein expression, normal unscheduled DNA synthesis, and impaired recovery of RNA synthesis in patient fibroblasts following UV-irradiation.
Conclusion: The study confirms the pathogenicity of a previously undescribed upstream intronic variant, highlighting the power of genome sequencing to identify noncoding variants. In addition, this report provides evidence for the utility of a combination approach of genome sequencing plus functional studies to provide diagnosis in a child for whom a lengthy diagnostic odyssey, including exome sequencing, was previously unrevealing.
Keywords: ERCC6; DNA repair; cockayne syndrome; whole-genome sequencing.
© 2021 The Authors. Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Friedman holds shares in Illumina and her Spouse is Founder and Principal of Friedman Bioventure, which holds a variety of publicly traded and private biotechnology interests. Other authors have no conflicts.
Figures

References
-
- Briggs, B., James, K. N., Chowdhury, S., Thornburg, C., Farnaes, L., Dimmock, D., & Kingsmore, S. F. (2018). Novel Factor XIII variant identified through whole‐genome sequencing in a child with intracranial hemorrhage. Cold Spring Harbor Molecular Case Studies, 4(6), a003525. 10.1101/mcs.a003525. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Farnaes, L., Hildreth, A., Sweeney, N. M., Clark, M. M., Chowdhury, S., Nahas, S., Cakicki, J. A., Benson, W., Kaplan, R. H., Kronick, R., Bainbridge, M. N., Friedman, J., Gold, J. J., Ding, Y., Veeraraghavan, N., Dimmock, D., & Kingsmore, S. F. (2018). Rapid whole‐genome sequencing decreases infant morbidity and cost of hospitalization. NPJ Genomic Medicine, 4(3), 10. 10.1038/s41525-018-0049-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

