Influence of NKG2C Genotypes on HIV Susceptibility and Viral Load Set Point
- PMID: 34076484
- PMCID: PMC8312870
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00417-21
Influence of NKG2C Genotypes on HIV Susceptibility and Viral Load Set Point
Abstract
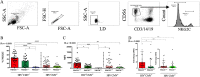
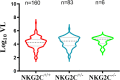
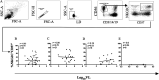
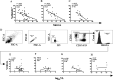
NKG2C is an activating NK cell receptor encoded by a gene having an unexpressed deletion variant. Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection expands a population of NKG2C+ NK cells with adaptive-like properties. Previous reports found that carriage of the deleted NKG2C- variant was more frequent in people living with HIV (PLWH) than in HIV- controls unexposed to HIV. The frequency of NKG2C+ NK cells positively correlated with HIV viral load (VL) in some studies and negatively correlated with VL in others. Here, we investigated the link between NKG2C genotype and HIV susceptibility and VL set point in PLWH. NKG2C genotyping was performed on 434 PLWH and 157 HIV-exposed seronegative (HESN) subjects. Comparison of the distributions of the three possible NKG2C genotypes in these populations revealed that the frequencies of NKG2C+/+ and NKG2C+/- carriers did not differ significantly between PLWH and HESN subjects, while that of NKG2C-/- carriers was higher in PLWH than in HESN subjects, in which none were found (P = 0.03, χ2 test). We were unable to replicate that carriage of at least 1 NKG2C- allele was more frequent in PLWH. Information on the pretreatment VL set point was available for 160 NKG2C+/+, 83 NKG2C+/-, and 6 NKG2C-/- PLWH. HIV VL set points were similar between NKG2C genotypes. The frequency of NKG2C+ CD3- CD14- CD19- CD56dim NK cells and the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of NKG2C expression on NK cells were higher on cells from CMV+ PLWH who carried 2, versus 1, NKG2C+ alleles. We observed no correlations between VL set point and either the frequency or the MFI of NKG2C expression. IMPORTANCE We compared NKG2C allele and genotype distributions in subjects who remained HIV uninfected despite multiple HIV exposures (HESN subjects) with those in the group PLWH. This allowed us to determine whether NKG2C genotype influenced susceptibility to HIV infection. The absence of the NKG2C-/- genotype among HESN subjects but not PLWH suggested that carriage of this genotype was associated with HIV susceptibility. We calculated the VL set point in a subset of 252 NKG2C-genotyped PLWH. We observed no between-group differences in the VL set point in carriers of the three possible NKG2C genotypes. No significant correlations were seen between the frequency or MFI of NKG2C expression on NK cells and VL set point in cytomegalovirus-coinfected PLWH. These findings suggested that adaptive NK cells played no role in establishing the in VL set point, a parameter that is a predictor of the rate of treatment-naive HIV disease progression.
Keywords: HIV exposed seronegative; HIV load set point; adaptive NK cells; human immunodeficiency virus; injection drug users; men who have sex with men; people living with HIV.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

