The molecular and epigenetic mechanisms of innate lymphoid cell (ILC) memory and its relevance for asthma
- PMID: 34076685
- PMCID: PMC8176441
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20201354
The molecular and epigenetic mechanisms of innate lymphoid cell (ILC) memory and its relevance for asthma
Abstract
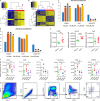
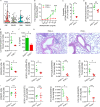
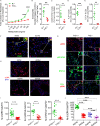
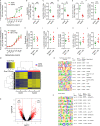
Repetitive exposure of Rag1-/- mice to the Alternaria allergen extract generated a form of memory that elicited an asthma-like response upon a subthreshold recall challenge 3-15 wk later. This memory was associated with lung ICOS+ST2+ ILC2s. Genetic, pharmacologic, and antibody-mediated inhibition and adoptive transfer established an essential role for ILC2s in memory-driven asthma. ATAC-seq demonstrated a distinct epigenetic landscape of memory ILC2s and identified Bach2 and AP1 (JunD and Fosl2) motifs as major drivers of altered gene accessibility. scRNA-seq, gene knockout, and signaling studies suggest that repetitive allergenic stress induces a gene repression program involving Nr4a2, Zeb1, Bach2, and JunD and a preparedness program involving Fhl2, FosB, Stat6, Srebf2, and MPP7 in memory ILC2s. A mutually regulated balance between these two programs establishes and maintains memory. The preparedness program (e.g., Fhl2) can be activated with a subthreshold cognate stimulation, which down-regulates repressors and activates effector pathways to elicit the memory-driven phenotype.
© 2021 Verma et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: M. Gorska reported a book contract with Springer Nature. The book will describe methods and protocols to study asthma. The book is currently in preparation. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures

Similar articles
-
BACH2 drives the development and function of group 2 innate lymphoid cells.Sci Adv. 2025 Aug;11(31):eads4323. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.ads4323. Epub 2025 Aug 1. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 40749046 Free PMC article.
-
Persistence of asthma requires multiple feedback circuits involving type 2 innate lymphoid cells and IL-33.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015 Jul;136(1):59-68.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.11.037. Epub 2015 Jan 21. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25617223 Free PMC article.
-
Allergen-Experienced Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells Acquire Memory-like Properties and Enhance Allergic Lung Inflammation.Immunity. 2016 Jul 19;45(1):198-208. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.06.017. Epub 2016 Jul 12. Immunity. 2016. PMID: 27421705
-
Innate lymphoid cells in asthma: Will they take your breath away?Eur J Immunol. 2016 Apr;46(4):795-806. doi: 10.1002/eji.201444557. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Eur J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26891006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells in Human Airway Disease.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016 Jan;16(1):8. doi: 10.1007/s11882-015-0581-6. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016. PMID: 26746844 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circular RNA circTmem241 drives group III innate lymphoid cell differentiation via initiation of Elk3 transcription.Nat Commun. 2022 Aug 11;13(1):4711. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32322-z. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35953472 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal asthma imprints fetal lung ILC2s via glucocorticoid signaling leading to worsened allergic airway inflammation in murine adult offspring.Nat Commun. 2025 Jan 13;16(1):631. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-55941-8. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39805834 Free PMC article.
-
ILC2 Diversity, Location, and Function in Pulmonary Disease.Immunol Rev. 2025 Jul;332(1):e70036. doi: 10.1111/imr.70036. Immunol Rev. 2025. PMID: 40454563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In-silico identification and prioritization of therapeutic targets of asthma.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 21;13(1):15706. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-42803-w. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37735578 Free PMC article.
-
The ins and outs of innate and adaptive type 2 immunity.Immunity. 2023 Apr 11;56(4):704-722. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2023.03.014. Immunity. 2023. PMID: 37044061 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agrawal, S., Agrawal A., Doughty B., Gerwitz A., Blenis J., Van Dyke T., and Pulendran B.. 2003. Cutting edge: different Toll-like receptor agonists instruct dendritic cells to induce distinct Th responses via differential modulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase-mitogen-activated protein kinase and c-Fos. J. Immunol. 171:4984–4989. 10.4049/jimmunol.171.10.4984 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ashraf, S., Hegazy Y.K., and Harmancey R.. 2019. Nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 2 inhibits activation of ERK signaling and cell growth in response to β-adrenergic stimulation in adult rat cardiomyocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 317:C513–C524. 10.1152/ajpcell.00526.2018 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bartolomé, R.A., García-Palmero I., Torres S., López-Lucendo M., Balyasnikova I.V., and Casal J.I.. 2015. IL13 Receptor α2 Signaling Requires a Scaffold Protein, FAM120A, to Activate the FAK and PI3K Pathways in Colon Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Res. 75:2434–2444. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-3650 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

