The molecular and epigenetic mechanisms of innate lymphoid cell (ILC) memory and its relevance for asthma
- PMID: 34076685
- PMCID: PMC8176441
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20201354
The molecular and epigenetic mechanisms of innate lymphoid cell (ILC) memory and its relevance for asthma
Abstract
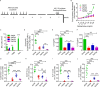
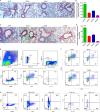
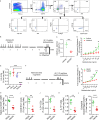
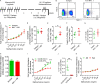
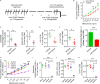
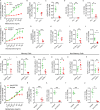
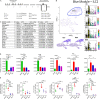
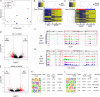
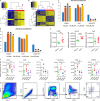
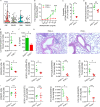
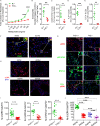
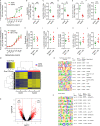
Repetitive exposure of Rag1-/- mice to the Alternaria allergen extract generated a form of memory that elicited an asthma-like response upon a subthreshold recall challenge 3-15 wk later. This memory was associated with lung ICOS+ST2+ ILC2s. Genetic, pharmacologic, and antibody-mediated inhibition and adoptive transfer established an essential role for ILC2s in memory-driven asthma. ATAC-seq demonstrated a distinct epigenetic landscape of memory ILC2s and identified Bach2 and AP1 (JunD and Fosl2) motifs as major drivers of altered gene accessibility. scRNA-seq, gene knockout, and signaling studies suggest that repetitive allergenic stress induces a gene repression program involving Nr4a2, Zeb1, Bach2, and JunD and a preparedness program involving Fhl2, FosB, Stat6, Srebf2, and MPP7 in memory ILC2s. A mutually regulated balance between these two programs establishes and maintains memory. The preparedness program (e.g., Fhl2) can be activated with a subthreshold cognate stimulation, which down-regulates repressors and activates effector pathways to elicit the memory-driven phenotype.
© 2021 Verma et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: M. Gorska reported a book contract with Springer Nature. The book will describe methods and protocols to study asthma. The book is currently in preparation. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures

References
-
- Agrawal, S., Agrawal A., Doughty B., Gerwitz A., Blenis J., Van Dyke T., and Pulendran B.. 2003. Cutting edge: different Toll-like receptor agonists instruct dendritic cells to induce distinct Th responses via differential modulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase-mitogen-activated protein kinase and c-Fos. J. Immunol. 171:4984–4989. 10.4049/jimmunol.171.10.4984 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ashraf, S., Hegazy Y.K., and Harmancey R.. 2019. Nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 2 inhibits activation of ERK signaling and cell growth in response to β-adrenergic stimulation in adult rat cardiomyocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 317:C513–C524. 10.1152/ajpcell.00526.2018 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bartolomé, R.A., García-Palmero I., Torres S., López-Lucendo M., Balyasnikova I.V., and Casal J.I.. 2015. IL13 Receptor α2 Signaling Requires a Scaffold Protein, FAM120A, to Activate the FAK and PI3K Pathways in Colon Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Res. 75:2434–2444. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-3650 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

