Precision Medicine on the Fly: Using Drosophila to Decipher Gene-Environment Interactions in Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 34076689
- PMCID: PMC8331128
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfab060
Precision Medicine on the Fly: Using Drosophila to Decipher Gene-Environment Interactions in Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
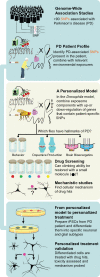
Big data approaches have profoundly influenced state-of-the-art in many fields of research, with toxicology being no exception. Here, we use Parkinson's disease as a window through which to explore the challenges of a dual explosion of metabolomic data addressing the myriad environmental exposures individuals experience and genetic analyses implicating many different loci as risk factors for disease. We argue that new experimental approaches are needed to convert the growing body of omics data into molecular mechanisms of disease that can be therapeutically targeted in specific patients. We outline one attractive strategy, which capitalizes on the rapid generation time and advanced molecular tools available in the fruit fly, Drosophila, to provide a platform for mechanistic dissection and drug discovery.
Keywords: Drosophila genetics; GWAS; Parkinson’s disease; exposome; gene-environment interactions; precision medicine.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society of Toxicology.All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Ascherio A., Schwarzschild M. A. (2016). The epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease: Risk factors and prevention. Lancet Neurol. 15, 1257–1272. - PubMed
-
- Betarbet R., Sherer T. B., MacKenzie G., Garcia-Osuna M., Panov A. V., Greenamyre J. T. (2000). Chronic systemic pesticide exposure reproduces features of Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 1301–1306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases