Fengycin A Analogues with Enhanced Chemical Stability and Antifungal Properties
- PMID: 34077216
- PMCID: PMC8289291
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.1c01387
Fengycin A Analogues with Enhanced Chemical Stability and Antifungal Properties
Abstract
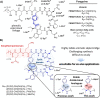
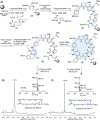
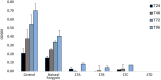
Fengycins are cyclic lipo-depsipeptides produced by Bacillus spp. that display potent antifungal properties but are chemically unstable. This instability has meant that no total synthesis of any fengycin has been published. Here we report the synthesis of fengycin A analogues that display enhanced antifungal properties and chemical stability under both basic and acidic conditions. The analogues prepared also demonstrate that the fengycin core structure can be modified and simplified without the loss of antifungal activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of cyclic lipopeptides produced by Bacillus vallismortis R2 and their antifungal activity against Alternaria alternata.J Appl Microbiol. 2017 Jan;122(1):139-152. doi: 10.1111/jam.13303. Epub 2016 Nov 23. J Appl Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 27665751
-
A Novel Variant of Narrow-Spectrum Antifungal Bacterial Lipopeptides That Strongly Inhibit Ganoderma boninense.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2018 Mar;10(1):110-117. doi: 10.1007/s12602-017-9334-2. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2018. PMID: 29101528
-
Diversification of Lipopeptide Analogues Drives Versatility in Biological Activities.J Agric Food Chem. 2025 Jan 15;73(2):1403-1416. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c11372. Epub 2025 Jan 6. J Agric Food Chem. 2025. PMID: 39760433 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in antimicrobial lipopeptide fengycin secreted by Bacillus: Structure, biosynthesis, antifungal mechanisms, and potential application in food preservation.Food Chem. 2025 Oct 15;489:144937. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2025.144937. Epub 2025 May 27. Food Chem. 2025. PMID: 40460478 Review.
-
Lipopeptides as the antifungal and antibacterial agents: applications in food safety and therapeutics.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:473050. doi: 10.1155/2015/473050. Epub 2015 Jan 6. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25632392 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Pseudomonas protegens and Bacillus subtilis Antimicrobials for Mitigation of Fuel Biocontamination.Biomolecules. 2025 Feb 4;15(2):227. doi: 10.3390/biom15020227. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40001530 Free PMC article.
-
Antagonistic mechanism of Bacillus velezensis HX0039 as a biocontrol agent against Trichoderma virens-induced "Sanghuang" green mold.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025 Aug 20;91(8):e0000525. doi: 10.1128/aem.00005-25. Epub 2025 Jul 8. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40626662 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Evidences of Biosurfactant Production in Two Bacillus subtilis Strains MB415 and MB418 Isolated From Oil Contaminated Soil.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Apr 26;10:855762. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.855762. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35557861 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial Metabolites: A Sustainable Approach to Combat Plant Pests.Metabolites. 2025 Jun 19;15(6):418. doi: 10.3390/metabo15060418. Metabolites. 2025. PMID: 40559442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthetic studies with the brevicidine and laterocidine lipopeptide antibiotics including analogues with enhanced properties and in vivo efficacy.Chem Sci. 2022 Feb 23;13(12):3563-3570. doi: 10.1039/d2sc00143h. eCollection 2022 Mar 24. Chem Sci. 2022. PMID: 35432860 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cawoy H.; Bettiol W.; Fickers P.; Ongena M.. Bacillus-Based Biological Control of Plant Diseases. In Pesticides in the Modern World—Pesticides Use and Management; IntechOpen, 2011.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

