Correlation and integration of circulating miRNA and peripheral whole blood gene expression profiles in patients with venous thromboembolism
- PMID: 34077299
- PMCID: PMC8806583
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1935401
Correlation and integration of circulating miRNA and peripheral whole blood gene expression profiles in patients with venous thromboembolism
Abstract
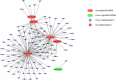
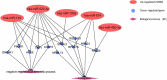
The main aim of this work was to evaluate differential expression and biological functions of circulating miRNA and whole peripheral blood (PB) genes in patients affected by venous thromboembolism (VTE) and in healthy subjects. Circulating miRNA sequences and PB expression profiles were obtained from GEO datasets. Ten miRNAs with the most significant differential expression rate (dif-miRNA) were subjected to miRbase to confirm their identity. Dif-miRNA targets were predicted by TargetScan and aligned with differentially expressed genes to obtain overlapping co-genes. Biological functions of co-genes were analyzed by Gene Ontology and KEGG analysis. Interaction network of dif-miRNAs, co-genes, and their downstream pathways were studied by analyzing protein-protein interaction (PPI) clusters (STRING) and determining the crucial hubs (Cytoscape).MiR-522-3p and miR-134 dif-miRNAs are involved in protein translation and apoptosis by regulating their respective co-genes in PB. Co-genes are present in nucleolus and extracellular exosomes and are involved in oxidative phosphorylation and ribosome/poly(A)-RNA organization. The predicted PPI network covered 107 clustered genes and 220 marginal joints, where ten hub genes participating in PPIs were found. All these hub genes were down-regulated in VTE patients. Our study identifies new miRNAs as potential biological markers and therapeutic targets for VTE.
Keywords: Circulating microRNA; biomarker candidates; genome-wide bioinformatic integration analysis; venous thromboembolism.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Bioinformatics Analysis and Identification of Genes and Molecular Pathways Involved in Venous Thromboembolism (VTE).Ann Vasc Surg. 2021 Jul;74:389-399. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2021.02.020. Epub 2021 Apr 2. Ann Vasc Surg. 2021. PMID: 33819580
-
Genetic correlations, shared risk genes and immunity landscapes between COVID-19 and venous thromboembolism: evidence from GWAS and bulk transcriptome data.Inflamm Res. 2024 Apr;73(4):619-640. doi: 10.1007/s00011-024-01857-w. Epub 2024 Mar 3. Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38433131
-
Bioinformatic analysis of peripheral blood miRNA of breast cancer patients in relation with anthracycline cardiotoxicity.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020 Feb 3;20(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s12872-020-01346-y. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020. PMID: 32013934 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA Expression Profiles, Target Genes, and Pathways in Intervertebral Disk Degeneration: A Meta-Analysis of 3 Microarray Studies.World Neurosurg. 2019 Jun;126:389-397. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.03.120. Epub 2019 Mar 20. World Neurosurg. 2019. PMID: 30904808 Review.
-
MiRNA 126 as a New Predictor Biomarker in Venous Thromboembolism of Persistent Residual Vein Obstruction: A Review of the Literature Plus a Pilot Study.Semin Thromb Hemost. 2021 Nov;47(8):982-991. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1726341. Epub 2021 Jul 9. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2021. PMID: 34243207 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploration of effective biomarkers for venous thrombosis embolism in Behçet's disease based on comprehensive bioinformatics analysis.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 10;14(1):15884. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66973-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38987624 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of four hub genes in venous thromboembolism via weighted gene coexpression network analysis.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021 Dec 3;21(1):577. doi: 10.1186/s12872-021-02409-4. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021. PMID: 34861826 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes in Central Nervous System Diseases: A Comprehensive Review of Emerging Research and Clinical Frontiers.Biomolecules. 2024 Nov 27;14(12):1519. doi: 10.3390/biom14121519. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39766226 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Raskob GE, Angchaisuksiri P, Blanco AN, et al. Thrombosis: a major contributor to global disease burden[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014;34(11):2363–2371. - PubMed
-
- Wendelboe AM, Raskob GE.. Global burden of thrombosis: epidemiologic aspects[J]. Circ Res. 2016;118(9):1340–1347. - PubMed
-
- Keller K, Hobohm L, Ebner M, et al. Trends in thrombolytic treatment and outcomes of acute pulmonary embolism in Germany. Eur Heart J. 2020;41(4):522–529. - PubMed
-
- Fesmire FM, Brown MD, Espinosa JA, et al. Critical issues in the evaluation and management of adult patients presenting to the emergency department with suspected pulmonary embolism. Ann Emerg Med. 2011;57(6):628–652. - PubMed
-
- Xu XF, Yang YH, Zhai ZG, et al. Prevalence and incidence of deep venous thrombosis among patients in medical intensive care unit. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2008;29(10):1034–1037. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
