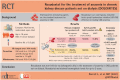
Roxadustat for the treatment of anaemia in chronic kidney disease patients not on dialysis: a Phase 3, randomized, open-label, active-controlled study (DOLOMITES)
- PMID: 34077510
- PMCID: PMC8396401
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfab191
Roxadustat for the treatment of anaemia in chronic kidney disease patients not on dialysis: a Phase 3, randomized, open-label, active-controlled study (DOLOMITES)
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: Roxadustat for the treatment of anaemia in chronic kidney disease patients not on dialysis: A Phase 3, randomised, open-label, active-controlled study (DOLOMITES).Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2022 Mar 25;37(4):805. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfab349. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2022. PMID: 35146511 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Roxadustat, an orally administered hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor, is being evaluated for treatment of anaemia of chronic kidney disease (CKD).
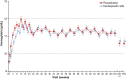
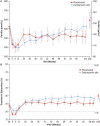
Methods: This randomized, open-label, active-controlled Phase 3 study compared roxadustat versus darbepoetin alfa (DA) in non-dialysis-dependent (NDD) CKD patients with anaemia for ≤104 weeks. Doses were titrated to correct and maintain haemoglobin (Hb) within 10.0-12.0 g/dL. The primary endpoint was Hb response in the full analysis set, defined as Hb ≥11.0 g/dL and Hb change from baseline (BL; CFB) ≥1.0 g/dL in patients with BL Hb >8.0 g/dL or CFB ≥2.0 g/dL in patients with BL Hb ≤8.0 g/dL during the first 24 weeks of treatment without rescue therapy (non-inferiority margin, -15%). Key secondary endpoints included change in low-density lipoprotein (LDL), time to first intravenous (IV) iron use, change in mean arterial pressure (MAP) and time to hypertension occurrence. Adverse events were assessed.
Results: Of 616 randomized patients (roxadustat, 323; DA, 293), 424 completed treatment (roxadustat, 215; DA, 209). Hb response with roxadustat was non-inferior to DA (roxadustat: 256/286, 89.5% versus DA: 213/273, 78.0%, difference 11.51%, 95% confidence interval 5.66-17.36%). Roxadustat maintained Hb for up to 2 years. Roxadustat was non-inferior to DA for change in MAP and time to occurrence of hypertension and superior for change in LDL and time to first IV iron use. Safety profiles were comparable between groups. Findings suggest that there was no difference between groups regarding the composite endpoints major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) and MACE+ [MACE: 0.81 (0.52-1.25), P = 0.339; MACE+: 0.90 (0.61-1.32), P = 0.583].
Conclusions: Roxadustat is a viable option to treat anaemia in NDD CKD patients maintaining Hb levels for up to 104 weeks.
Keywords: anaemia; chronic kidney disease; erythropoietin; haemoglobin.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA.
Figures



References
-
- Fishbane S, Spinowitz B.. Update on anemia in ESRD and earlier stages of CKD: core curriculum 2018. Am J Kidney Dis 2018; 71: 423–435 - PubMed
-
- Locatelli F, Fishbane S, Block GA. et al. Targeting hypoxia-inducible factors for the treatment of anemia in chronic kidney disease patients. Am J Nephrol 2017; 45: 187–199 - PubMed
-
- Pfeffer MA, Burdmann EA, Chen CY. et al. A trial of darbepoetin alfa in type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med 2009; 361: 2019–2032 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

