Identification of a population of peripheral sensory neurons that regulates blood pressure
- PMID: 34077727
- PMCID: PMC8187988
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109191
Identification of a population of peripheral sensory neurons that regulates blood pressure
Abstract
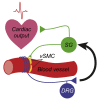
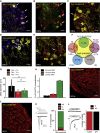
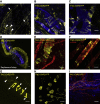
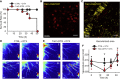
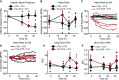
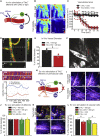
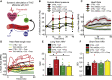
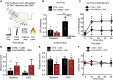
The vasculature is innervated by a network of peripheral afferents that sense and regulate blood flow. Here, we describe a system of non-peptidergic sensory neurons with cell bodies in the spinal ganglia that regulate vascular tone in the distal arteries. We identify a population of mechanosensitive neurons, marked by tropomyosin receptor kinase C (TrkC) and tyrosine hydroxylase in the dorsal root ganglia, which projects to blood vessels. Local stimulation of TrkC neurons decreases vessel diameter and blood flow, whereas systemic activation increases systolic blood pressure and heart rate variability via the sympathetic nervous system. Ablation of the neurons provokes variability in local blood flow, leading to a reduction in systolic blood pressure, increased heart rate variability, and ultimately lethality within 48 h. Thus, a population of TrkC+ sensory neurons forms part of a sensory-feedback mechanism that maintains cardiovascular homeostasis through the autonomic nervous system.
Keywords: DRG; TH; TrkC; blood pressure; cardiovascular homeostasis; peripheral nervous system.
Copyright © 2021 European Molecular Biology Laboratory. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Abrahamsen B., Zhao J., Asante C.O., Cendan C.M., Marsh S., Martinez-Barbera J.P., Nassar M.A., Dickenson A.H., Wood J.N. The cell and molecular basis of mechanical, cold, and inflammatory pain. Science. 2008;321:702–705. - PubMed
-
- Adelson D.W., Wei J.Y., Kruger L. Warm-sensitive afferent splanchnic C-fiber units in vitro. J. Neurophysiol. 1997;77:2989–3002. - PubMed
-
- Albrecht P.J., Hou Q., Argoff C.E., Storey J.R., Wymer J.P., Rice F.L. Excessive peptidergic sensory innervation of cutaneous arteriole-venule shunts (AVS) in the palmar glabrous skin of fibromyalgia patients: implications for widespread deep tissue pain and fatigue. Pain Med. 2013;14:895–915. - PubMed
-
- Anitescu M. Ischemic pain. In: Cheng J., Rosenquist R.W., editors. Fundamentals of Pain Medicine. Springer International Publishing; 2018. pp. 141–151.
-
- Arcourt A., Gorham L., Dhandapani R., Prato V., Taberner F.J., Wende H., Gangadharan V., Birchmeier C., Heppenstall P.A., Lechner S.G. Touch receptor-derived sensory information alleviates acute pain signaling and fine-tunes nociceptive reflex coordination. Neuron. 2017;93:179–193. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

