D-chiro-inositol, an aromatase down-modulator, increases androgens and reduces estrogens in male volunteers: a pilot study
- PMID: 34078260
- PMCID: PMC8173878
- DOI: 10.1186/s12610-021-00131-x
D-chiro-inositol, an aromatase down-modulator, increases androgens and reduces estrogens in male volunteers: a pilot study
Abstract
Background: Androgen deficiency affects men in the adulthood, causing several harmful effects at the reproductive and behavioural levels. Since aromatase is an enzyme that catalyses the conversion of androgens to estrogens, and it is responsible for an adequate balance of both sex hormones in males and females, the administration of molecules acting as down modulators may contribute to restore an abnormal enzymatic activity. A prospective pilot study was carried out to investigate the effect of D-chiro-inositol, a putative aromatase down-modulator, on serum levels of testosterone, estradiol, estrone, dehydroepiandrosterone and epiandrosterone from a group of adult male volunteers. Glucose, insulin, follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, inhibin B, D-chiro-inositol and myo-inositol serum levels were also measured.
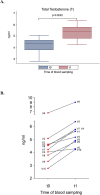
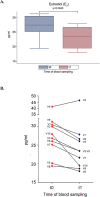
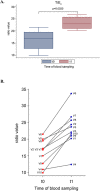
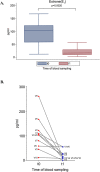
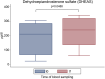
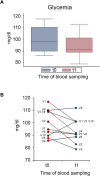
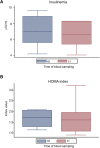
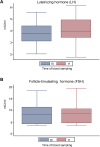
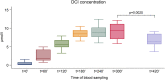
Results: Male volunteers were selected according to age and body mass index. Subjects with altered glycemia and/or hormonal status, due to advanced age or abnormal weight, were enrolled in the study. Each of the 10 volunteers enrolled took oral D-chiro-inositol (1 g/day) for 1 month. Serum assays of selected markers were performed at baseline (control) and after treatment. D-chiro-inositol administration was associated to reduced serum levels of estrone (- 85.0%) and estradiol (- 14.4%), and increased serum levels of testosterone (+ 23.4%) and dehydroepiandrosterone (+ 13.8%). In addition, epiandrosterone levels were higher (+39%) after treatment. On the other hand, follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone and inhibin B did not change. A trend toward a decrease of glycemia, insulinemia and Homeostatic Model Assessment index was observed after D-chiro-inositol treatment, although differences did not reach statistical significance. D-chiro-inositol treatment did not cause any noticeable adverse effect.
Conclusions: Increased androgens and decreased estrogens seem to confirm that D-chiro-inositol acts as an aromatase down-modulator, but with a still unknown mechanism of action. This pilot study opens up new perspectives of research and therapeutic applications for D-chiro-inositol at different dosages and length of treatment. Authorization number 005/2020 released by the Local Ethics Committee of Alma Res Fertility Center, Rome.
Trial registration number: NCT04615767 (registry: ClinicalTrials.gov) Date of registration: November 3, 2020.
RéSUMé: CONTEXTE: L’insuffisance en androgènes affecte les hommes à l’âge adulte, causant plusieurs effets nocifs aux niveaux reproductif et comportemental. Puisque l’aromatase est. une enzyme qui catalyse la conversion des androgènes en œstrogènes, et qu’elle est. responsable d’un équilibre adéquat des hormones sexuelles chez les hommes et les femmes, l’administration de molécules agissant comme freinateurs peut contribuer à restaurer une activité enzymatique anormale. Une étude prospective pilote a été menée pour étudier l’effet du D-chiro-inositol, un potentiel freinateur de l’aromatase, sur les taux sériques de testostérone, estradiol, estrone, déhydroépiandrostérone et d’épiandrostérone d’un groupe d’hommes adultes volontaires. Le glucose, l’insuline, l’hormone folliculostimulante, l’hormone lutéinisante, l’inhibine B, le D-chiro-inositol et les taux sériques de myo-inositol ont également été mesurés. RéSULTATS: Les hommes volontaires ont été sélectionnés selon l’âge et l’indice de masse corporelle. Les hommes qui présentaient une glycémie et/ou un statut hormonal altérés en raison d’un âge avancé ou d’un poids anormal, ont été inclus dans l’étude. Chacun des 10 volontaires enrôlés a pris du D-chiro-inositol (1 g/jour) par voie orale pendant un mois. Des dosages sériques des marqueurs sélectionnés ont été réalisés avant (témoin) et après le traitement. L’administration de D-chiro-inositol a été associée à une réduction des taux sériques de l’estrone (− 85.0%) et de l’estradiol (− 14,4%), et a une augmentation des taux sériques de testostérone (+ 23,4%) et de déhydroépiandrostérone (+ 13,8%). En outre, les taux d’épiandrostérone étaient plus élevés (39%) après le traitement. D’autre part, les taux d’hormone folliculostimulante, d’hormone lutéinisante et d’inhibine B n’ont pas été modifiés. Une tendance à la diminution de la glycémie, de l’insulinémie et de l’indice d’évaluation du modèle homéostatique a été observée après traitement par D-chiro-inositol, bien que les différences n’aient pas atteint une signification statistique. Le traitement par D-chiro-inositol n’a causé aucun effet indésirable notable. CONCLUSIONS: L’augmentation des androgènes et la diminution des œstrogènes semblent confirmer que le D-chiro-inositol agit comme un freinateur de l’aromatase, mais avec un mécanisme d’action encore inconnu. Cette étude pilote ouvre de nouvelles perspectives de recherche et d’applications thérapeutiques pour le D-chiro-inositol à différents dosages et durées de traitement.
Keywords: DHEAS; Epiandrosterone; Estradiol; Estrone; Glycemia; HOMA index; Inhibin B; Insulinemia; Testosterone.
Conflict of interest statement
Vittorio Unfer is an employee at Lo.Li. Pharma srl. (Rome, Italy). The other authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-Lasting Therapies with High Doses of D-chiro-inositol: The Downside.J Clin Med. 2023 Jan 3;12(1):390. doi: 10.3390/jcm12010390. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36615188 Free PMC article.
-
The use of D-chiro-Inositol in clinical practice.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021 Jan;25(1):438-446. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202101_24412. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33506934 Review.
-
Inositols: From Established Knowledge to Novel Approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 30;22(19):10575. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910575. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
<sc>d</sc>-Chiro-Inositol in Clinical Practice: A Perspective from the Experts Group on Inositol in Basic and Clinical Research (EGOI).Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2024;89(4):284-294. doi: 10.1159/000536081. Epub 2024 Feb 19. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2024. PMID: 38373412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Inositols in the Hyperandrogenic Phenotypes of PCOS: A Re-Reading of Larner's Results.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 27;24(7):6296. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076296. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047265 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
D-Chiro-Inositol improves testosterone levels in older hypogonadal men with low-normal testosterone: a pilot study.Basic Clin Androl. 2021 Nov 12;31(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s12610-021-00146-4. Basic Clin Androl. 2021. PMID: 34763665 Free PMC article.
-
New Perspectives on Nutraceutical Insulin Sensitizing Agents in the Treatment of Psoriasis and Other Dermatological Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 4;26(15):7538. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157538. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel insights into D-Pinitol based therapies: a link between tau hyperphosphorylation and insulin resistance.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Feb;19(2):289-295. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.379015. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 37488880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of Myo-Inositol and Microlipodispersed Magnesium in Androgen-Dependent Dermatological Diseases: A Retrospective Study.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Feb 13;18(2):251. doi: 10.3390/ph18020251. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40006064 Free PMC article.
-
Stereoselective Voltammetric Biosensor for Myo-Inositol and D-Chiro-Inositol Recognition.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Nov 16;23(22):9211. doi: 10.3390/s23229211. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38005597 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benyi E, Savendahl L. The physiology of childhood growth: hormonal regulation. Horm Res Paediatr. 2017;88(1):6–14. - PubMed
-
- Vermeulen A, Kaufman JM, Goemaere S, van Pottelberg I. Estradiol in elderly men. Aging Male. 2002;5(2):98–102. - PubMed
-
- Muller M, den Tonkelaar I, Thijssen JH, Grobbee DE, van der Schouw YT. Endogenous sex hormones in men aged 40-80 years. Eur J Endocrinol. 2003;149(6):583–589. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

