Using nontargeted LC-MS metabolomics to identify the Association of Biomarkers in pig feces with feed efficiency
- PMID: 34078468
- PMCID: PMC8170940
- DOI: 10.1186/s40813-021-00219-w
Using nontargeted LC-MS metabolomics to identify the Association of Biomarkers in pig feces with feed efficiency
Abstract
Background: Improving feed efficiency is economically and environmentally beneficial in the pig industry. A deeper understanding of feed efficiency is essential on many levels for its highly complex nature. The aim of this project is to explore the relationship between fecal metabolites and feed efficiency-related traits, thereby identifying metabolites that may assist in the screening of the feed efficiency of pigs.
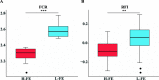
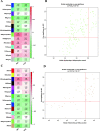
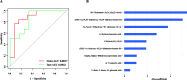
Results: We performed fecal metabolomics analysis on 50 individuals selected from 225 Duroc x (Landrace x Yorkshire) (DLY) commercial pigs, 25 with an extremely high feed efficiency and 25 with an extremely low feed efficiency. A total of 6749 and 5644 m/z features were detected in positive and negative ionization modes by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC/MS). Regrettably, the PCA could not classify the the samples accurately. To improve the classification, OPLS-DA was introduced. However, the predictive ability of the OPLS-DA model did not perform well. Then, through weighted coexpression network analysis (WGCNA), we found that one module in each positive and negative mode was related to residual feed intake (RFI), and six and three metabolites were further identified. The nine metabolites were found to be involved in multiple metabolic pathways, including lipid metabolism (primary bile acid synthesis, linoleic acid metabolism), vitamin D, glucose metabolism, and others. Then, Lasso regression analysis was used to evaluate the importance of nine metabolites obtained by the annotation process.
Conclusions: Altogether, this study provides new insights for the subsequent evaluation of commercial pig feed efficiency through small molecule metabolites, but also provide a reference for the development of new feed additives.
Keywords: Feed efficiency; LC-MS; Pig; WGCNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lipids and organic acids in three gut locations affect feed efficiency of commercial pigs as revealed by LC-MS-based metabolomics.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 8;11(1):7746. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87322-8. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33833350 Free PMC article.
-
Using Untargeted LC-MS Metabolomics to Identify the Association of Biomarkers in Cattle Feces with Marbling Standard Longissimus Lumborum.Animals (Basel). 2022 Aug 30;12(17):2243. doi: 10.3390/ani12172243. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36077963 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Epistatic Interaction Networks Affecting Feed Efficiency in Duroc and Landrace Pigs.Front Genet. 2020 Feb 28;11:121. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00121. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32184802 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omics unveils tryptophan metabolic pathway as a key pathway influencing residual feed intake in Duroc swine.Front Vet Sci. 2024 May 29;11:1403493. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1403493. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 38868499 Free PMC article.
-
Review: Biological determinants of between-animal variation in feed efficiency of growing beef cattle.Animal. 2018 Dec;12(s2):s321-s335. doi: 10.1017/S1751731118001489. Epub 2018 Aug 24. Animal. 2018. PMID: 30139392 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of the Probiotic, Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus, as a Substitute for Antibiotics on the Gastrointestinal Tract Microbiota and Metabolomics Profile of Female Growing-Finishing Pigs.Animals (Basel). 2022 Jul 11;12(14):1778. doi: 10.3390/ani12141778. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35883325 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Heterozygosity and Genome-Wide Analysis of Heterozygosity Regions in Two Duroc Pig Populations.Front Genet. 2022 Jan 27;12:812456. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.812456. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35154256 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-Omics Integration in Mice With Parkinson's Disease and the Intervention Effect of Cyanidin-3-O-Glucoside.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Apr 29;14:877078. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.877078. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35572129 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of Omics Technology for Livestock Selection and Improvement.Front Genet. 2022 Jun 2;13:774113. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.774113. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35719396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Networks and Graphs Discovery in Metabolomics Data Analysis and Interpretation.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Mar 8;9:841373. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.841373. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35350714 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Saintilan R, Mérour I, Schwob S, Sellier P, Bidanel J, Gilbert H. Genetic parameters and halothane genotype effect for residual feed intake in Piétrain growing pigs. Livest Sci. 2011;142(1–3):203–209. doi: 10.1016/j.livsci.2011.07.013. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

