Silent zero TE MR neuroimaging: Current state-of-the-art and future directions
- PMID: 34078538
- PMCID: PMC7616227
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pnmrs.2021.03.002
Silent zero TE MR neuroimaging: Current state-of-the-art and future directions
Abstract
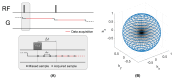
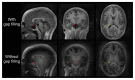
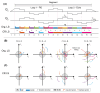
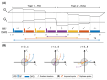
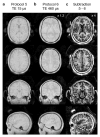
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scanners produce loud acoustic noise originating from vibrational Lorentz forces induced by rapidly changing currents in the magnetic field gradient coils. Using zero echo time (ZTE) MRI pulse sequences, gradient switching can be reduced to a minimum, which enables near silent operation.Besides silent MRI, ZTE offers further interesting characteristics, including a nominal echo time of TE = 0 (thus capturing short-lived signals from MR tissues which are otherwise MR-invisible), 3D radial sampling (providing motion robustness), and ultra-short repetition times (providing fast and efficient scanning).In this work we describe the main concepts behind ZTE imaging with a focus on conceptual understanding of the imaging sequences, relevant acquisition parameters, commonly observed image artefacts, and image contrasts. We will further describe a range of methods for anatomical and functional neuroimaging, together with recommendations for successful implementation.
Keywords: Neuroimaging; Silent MRI; Zero Echo Time (ZTE).
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: FW and ABS: employees of General Electric Healthcare. GJB receives honoraria from GE Healthcare for teaching. EL, NLD, TCW, DJL, FZ, SCRW: None.
Figures


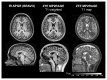
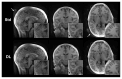





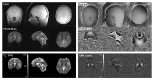
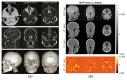

References
-
- Mansfield P, Glover PM, Beaumont J. Sound generation in gradient coil structures for MRI. Magn Reson Med. 1998;39:539–550. - PubMed
-
- McJury MJ. Acoustic noise levels generated during high field MR imaging. Clin Radiol. 1995;50:331–334. - PubMed
-
- Jin C, Li H, Li X, Wang M, Liu C, Guo J, Yang J. Temporary hearing threshold shift in healthy volunteers with hearing protection caused by acoustic noise exposure during 3-T multisequence MR neuroimaging. Radiology. 2018;286:602–608. - PubMed
-
- Mcjury M, Shellock FG. Auditory Noise Associated With MR Procedures: A Review. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2000;12:37–45. - PubMed
-
- Foster JR, Hall DA, Summerfield AQ, Palmer AR, Bowtell RW. Sound-level measurements and calculations of safe noise dosage during EPI at 3 T. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2000;12:157–163. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

