An antibody against L1 cell adhesion molecule inhibits cardiotoxicity by regulating persistent DNA damage
- PMID: 34078883
- PMCID: PMC8172563
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-23478-1
An antibody against L1 cell adhesion molecule inhibits cardiotoxicity by regulating persistent DNA damage
Abstract
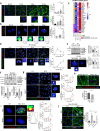
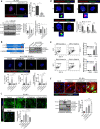
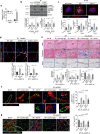
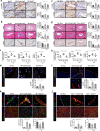
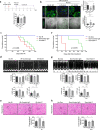
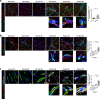
Targeting the molecular pathways underlying the cardiotoxicity associated with thoracic irradiation and doxorubicin (Dox) could reduce the morbidity and mortality associated with these anticancer treatments. Here, we find that vascular endothelial cells (ECs) with persistent DNA damage induced by irradiation and Dox treatment exhibit a fibrotic phenotype (endothelial-mesenchymal transition, EndMT) correlating with the colocalization of L1CAM and persistent DNA damage foci. We demonstrate that treatment with the anti-L1CAM antibody Ab417 decreases L1CAM overexpression and nuclear translocation and persistent DNA damage foci. We show that in whole-heart-irradiated mice, EC-specific p53 deletion increases vascular fibrosis and the colocalization of L1CAM and DNA damage foci, while Ab417 attenuates these effects. We also demonstrate that Ab417 prevents cardiac dysfunction-related decrease in fractional shortening and prolongs survival after whole-heart irradiation or Dox treatment. We show that cardiomyopathy patient-derived cardiovascular ECs with persistent DNA damage show upregulated L1CAM and EndMT, indicating clinical applicability of Ab417. We conclude that controlling vascular DNA damage by inhibiting nuclear L1CAM translocation might effectively prevent anticancer therapy-associated cardiotoxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Liposomal doxorubicin attenuates cardiotoxicity via induction of interferon-related DNA damage resistance.Cardiovasc Res. 2020 Apr 1;116(5):970-982. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvz192. Cardiovasc Res. 2020. PMID: 31346605
-
Adiponectin agonist ADP355 ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by decreasing cardiomyocyte apoptosis and oxidative stress.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Dec 10;533(3):304-312. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.09.035. Epub 2020 Sep 18. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 32958254
-
Cardiomyocytes, cardiac endothelial cells and fibroblasts contribute to anthracycline-induced cardiac injury through RAS-homologous small GTPases RAC1 and CDC42.Pharmacol Res. 2024 May;203:107165. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107165. Epub 2024 Mar 30. Pharmacol Res. 2024. PMID: 38561112
-
Transcriptional regulation of endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cardiac fibrosis: role of myocardin-related transcription factor A and activating transcription factor 3.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2017 Oct;95(10):1263-1270. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2016-0634. Epub 2017 Jul 7. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28686848 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of endothelial remodeling under doxorubicin treatment.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Jun;162:114576. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114576. Epub 2023 Mar 28. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 36989721 Review.
Cited by
-
The Impairment of Cell Metabolism by Cardiovascular Toxicity of Doxorubicin Is Reversed by Bergamot Polyphenolic Fraction Treatment in Endothelial Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 11;23(16):8977. doi: 10.3390/ijms23168977. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012238 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into mitochondrial quality control in anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity: molecular mechanisms, therapeutic targets, and natural products.Int J Biol Sci. 2025 Jan 1;21(2):507-523. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.103810. eCollection 2025. Int J Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39781459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
2-Methoxyestradiol Inhibits Radiation-Induced Skin Injuries.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 10;23(8):4171. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084171. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35456989 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of bimetal MOFs for rapid removal of doxorubicin in water by advanced oxidation method.RSC Adv. 2022 Dec 14;12(55):35666-35675. doi: 10.1039/d2ra06623h. eCollection 2022 Dec 12. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 36545067 Free PMC article.
-
miR-488-3p Protects Cardiomyocytes against Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity by Inhibiting CyclinG1.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Feb 10;2022:5184135. doi: 10.1155/2022/5184135. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35186188 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

