RNA atlas of human bacterial pathogens uncovers stress dynamics linked to infection
- PMID: 34078900
- PMCID: PMC8172932
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-23588-w
RNA atlas of human bacterial pathogens uncovers stress dynamics linked to infection
Abstract
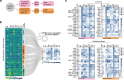
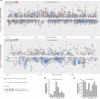
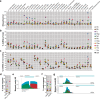
Bacterial processes necessary for adaption to stressful host environments are potential targets for new antimicrobials. Here, we report large-scale transcriptomic analyses of 32 human bacterial pathogens grown under 11 stress conditions mimicking human host environments. The potential relevance of the in vitro stress conditions and responses is supported by comparisons with available in vivo transcriptomes of clinically important pathogens. Calculation of a probability score enables comparative cross-microbial analyses of the stress responses, revealing common and unique regulatory responses to different stresses, as well as overlapping processes participating in different stress responses. We identify conserved and species-specific 'universal stress responders', that is, genes showing altered expression in multiple stress conditions. Non-coding RNAs are involved in a substantial proportion of the responses. The data are collected in a freely available, interactive online resource (PATHOgenex).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
RNA-Sequencing Analyses of Small Bacterial RNAs and their Emergence as Virulence Factors in Host-Pathogen Interactions.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 27;21(5):1627. doi: 10.3390/ijms21051627. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32120885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulating Bacterial Virulence with RNA.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2017 Sep 8;71:263-280. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-030117-020335. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28886688 Review.
-
Microarray analysis of bacterial pathogenicity.Adv Microb Physiol. 2002;46:1-45. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(02)46001-8. Adv Microb Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12073651 Review.
-
sRNA-mediated control in bacteria: An increasing diversity of regulatory mechanisms.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2020 May;1863(5):194504. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2020.194504. Epub 2020 Mar 9. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2020. PMID: 32061884 Review.
-
The extracellular vesicle generation paradox: a bacterial point of view.EMBO J. 2021 Nov 2;40(21):e108174. doi: 10.15252/embj.2021108174. Epub 2021 Oct 11. EMBO J. 2021. PMID: 34636061 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Yersiniomics, a Multi-Omics Interactive Database for Yersinia Species.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 27;11(2):e0382622. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03826-22. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36847572 Free PMC article.
-
Human whole blood influences the expression of Acinetobacter baumannii genes related to translation and siderophore production.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 24;20(7):e0326330. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0326330. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40705813 Free PMC article.
-
Non-antibiotics disrupt colonization resistance against enteropathogens.Nature. 2025 Aug;644(8076):497-505. doi: 10.1038/s41586-025-09217-2. Epub 2025 Jul 16. Nature. 2025. PMID: 40670795 Free PMC article.
-
The impacts of viral infection and subsequent antimicrobials on the microbiome-resistome of growing pigs.Microbiome. 2022 Aug 4;10(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s40168-022-01312-0. Microbiome. 2022. PMID: 35922873 Free PMC article.
-
Making sense of drug-efflux transporters in the physiological environment.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2022 Oct;69:102179. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2022.102179. Epub 2022 Jul 23. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35882103 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

