NEK9 regulates primary cilia formation by acting as a selective autophagy adaptor for MYH9/myosin IIA
- PMID: 34078910
- PMCID: PMC8172835
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-23599-7
NEK9 regulates primary cilia formation by acting as a selective autophagy adaptor for MYH9/myosin IIA
Abstract
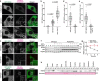
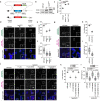
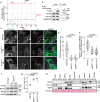
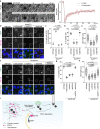
Autophagy regulates primary cilia formation, but the underlying mechanism is not fully understood. In this study, we identify NIMA-related kinase 9 (NEK9) as a GABARAPs-interacting protein and find that NEK9 and its LC3-interacting region (LIR) are required for primary cilia formation. Mutation in the LIR of NEK9 in mice also impairs in vivo cilia formation in the kidneys. Mechanistically, NEK9 interacts with MYH9 (also known as myosin IIA), which has been implicated in inhibiting ciliogenesis through stabilization of the actin network. MYH9 accumulates in NEK9 LIR mutant cells and mice, and depletion of MYH9 restores ciliogenesis in NEK9 LIR mutant cells. These results suggest that NEK9 regulates ciliogenesis by acting as an autophagy adaptor for MYH9. Given that the LIR in NEK9 is conserved only in land vertebrates, the acquisition of the autophagic regulation of the NEK9-MYH9 axis in ciliogenesis may have possible adaptive implications for terrestrial life.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
NIMA-related kinase 9-mediated phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated LC3B protein at Thr-50 suppresses selective autophagy of p62/sequestosome 1.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jan 31;295(5):1240-1260. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.010068. Epub 2019 Dec 19. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 31857374 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis of the autophagy-related LC3/Atg13 LIR complex: recognition and interaction mechanism.Structure. 2014 Jan 7;22(1):47-58. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2013.09.023. Epub 2013 Nov 27. Structure. 2014. PMID: 24290141
-
Recessive NEK9 mutation causes a lethal skeletal dysplasia with evidence of cell cycle and ciliary defects.Hum Mol Genet. 2016 May 1;25(9):1824-35. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw054. Epub 2016 Feb 21. Hum Mol Genet. 2016. PMID: 26908619
-
Reciprocal Regulation between Primary Cilia and mTORC1.Genes (Basel). 2020 Jun 26;11(6):711. doi: 10.3390/genes11060711. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32604881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NEK8, a NIMA-family protein kinase at the core of the ciliary INV complex.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Apr 7;23(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02143-w. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 40189576 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
HOPS-dependent lysosomal fusion controls Rab19 availability for ciliogenesis in polarized epithelial cells.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 8:2023.02.07.527563. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.07.527563. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: J Cell Sci. 2024 Mar 1;137(5):jcs261047. doi: 10.1242/jcs.261047. PMID: 36798155 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
An actin filament branching surveillance system regulates cell cycle progression, cytokinesis and primary ciliogenesis.Nat Commun. 2023 Mar 27;14(1):1687. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37340-z. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36973243 Free PMC article.
-
The function of the ATG8 in the cilia and cortical microtubule maintenance of Euplotes amieti.Protoplasma. 2024 Nov;261(6):1127-1145. doi: 10.1007/s00709-024-01957-8. Epub 2024 May 20. Protoplasma. 2024. PMID: 38769089
-
USP19 potentiates autophagic cell death via inhibiting mTOR pathway through deubiquitinating NEK9 in pancreatic cancer.Cell Death Differ. 2025 Apr;32(4):702-713. doi: 10.1038/s41418-024-01426-y. Epub 2024 Dec 3. Cell Death Differ. 2025. PMID: 39627360
-
Identification of mitophagy-related genes in patients with acute myocardial infarction.Hereditas. 2025 Apr 26;162(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s41065-025-00424-5. Hereditas. 2025. PMID: 40287718 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

