Evaluation of a collaborative model for successful implementation of a National CD4 enumeration EQA program in Cameroon
- PMID: 34078982
- PMCID: PMC8172912
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-91015-7
Evaluation of a collaborative model for successful implementation of a National CD4 enumeration EQA program in Cameroon
Abstract
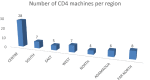
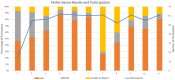
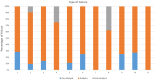
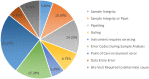
Participation in an EQA program is critical to the quality assurance process. Reliable and precise CD4 T-cells enumeration are essential to improve the clinical management of patients by evaluating the disease progression and by monitoring the effectiveness of ART in HIV-patients. The CIRCB, CD4 reference laboratory, in collaboration with the Canadian QASI-program, recruited sites, distributed and analyzed CD4-panels in 61 sites across Cameroon. A trend and performance analysis in the pre-analytical, analytical and post-analytical phases was performed. Continuous training and corrective actions carried out from 2014 to 2018 increased the number of participating sites from 15 to 61 sites, the number of unacceptable results decreased from 50 to 10%. Specific challenges included errors in pre analytic (17.5%), analytic (77.0%) and post-analytic (5.5%) phases. This EQA requires the application of good laboratory practices, fluidic communication between all the stakeholders, continuous training, application of specific on-site corrective measures, and timely equipment maintenance in order to avoid repetitive errors and to increase laboratory performance. It could be extended to other HIV-1 testing like viral load and EID point-of-care. Partnership with QASI serve as a model for implementation of a successful EQA model for resource limited countries wanting to implement EQA for HIV testing and monitoring in alignment with 90-90-90 targets.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- UNAIDS. UNAIDS Data 2019 [Internet]. UNAIDS; https://www.unaidsorg/en/resources/documents/2019/2019-UNAIDS-data (2019).
-
- UNAIDS. 90–90–90 An ambitious treatment target to help end the AIDS epidemic. Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) (2014).
-
- Organization WH. Consolidated guidelines on the use of antiretroviral drugs for treating and preventing HIV infection. Worl Health Org. 2016;12:1361–1364. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

