SOG1 transcription factor promotes the onset of endoreduplication under salinity stress in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 34079040
- PMCID: PMC8172935
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-91293-1
SOG1 transcription factor promotes the onset of endoreduplication under salinity stress in Arabidopsis
Retraction in
-
Retraction Note: SOG1 transcription factor promotes the onset of endoreduplication under salinity stress in Arabidopsis.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 21;14(1):4282. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-54831-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38383729 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
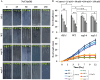
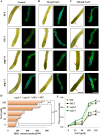
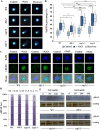
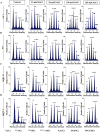
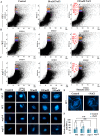
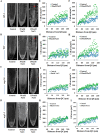
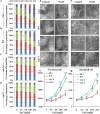
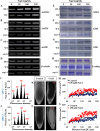
As like in mammalian system, the DNA damage responsive cell cycle checkpoint functions play crucial role for maintenance of genome stability in plants through repairing of damages in DNA and induction of programmed cell death or endoreduplication by extensive regulation of progression of cell cycle. ATM and ATR (ATAXIA-TELANGIECTASIA-MUTATED and -RAD3-RELATED) function as sensor kinases and play key role in the transmission of DNA damage signals to the downstream components of cell cycle regulatory network. The plant-specific NAC domain family transcription factor SOG1 (SUPPRESSOR OF GAMMA RESPONSE 1) plays crucial role in transducing signals from both ATM and ATR in presence of double strand breaks (DSBs) in the genome and found to play crucial role in the regulation of key genes involved in cell cycle progression, DNA damage repair, endoreduplication and programmed cell death. Here we report that Arabidopsis exposed to high salinity shows generation of oxidative stress induced DSBs along with the concomitant induction of endoreduplication, displaying increased cell size and DNA ploidy level without any change in chromosome number. These responses were significantly prominent in SOG1 overexpression line than wild-type Arabidopsis, while sog1 mutant lines showed much compromised induction of endoreduplication under salinity stress. We have found that both ATM-SOG1 and ATR-SOG1 pathways are involved in the salinity mediated induction of endoreduplication. SOG1was found to promote G2-M phase arrest in Arabidopsis under salinity stress by downregulating the expression of the key cell cycle regulators, including CDKB1;1, CDKB2;1, and CYCB1;1, while upregulating the expression of WEE1 kinase, CCS52A and E2Fa, which act as important regulators for induction of endoreduplication. Our results suggest that Arabidopsis undergoes endoreduplicative cycle in response to salinity induced DSBs, showcasing an adaptive response in plants under salinity stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
An insight into the mechanism of DNA damage response in plants- role of SUPPRESSOR OF GAMMA RESPONSE 1: An overview.Mutat Res. 2020 Jan-Apr;819-820:111689. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2020.111689. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Mutat Res. 2020. PMID: 32004947 Review.
-
Programmed induction of endoreduplication by DNA double-strand breaks in Arabidopsis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jun 14;108(24):10004-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1103584108. Epub 2011 May 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21613568 Free PMC article.
-
Aluminum-Dependent Terminal Differentiation of the Arabidopsis Root Tip Is Mediated through an ATR-, ALT2-, and SOG1-Regulated Transcriptional Response.Plant Cell. 2015 Sep;27(9):2501-15. doi: 10.1105/tpc.15.00172. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Plant Cell. 2015. PMID: 26320227 Free PMC article.
-
SOG1 and BRCA1 Interdependently Regulate RAD54 Expression for Repairing Salinity-Induced DNA Double-Strand Breaks in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell Physiol. 2024 May 30;65(5):708-728. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcae008. Plant Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38242160
-
SOG1: a master regulator of the DNA damage response in plants.Genes Genet Syst. 2016;90(4):209-16. doi: 10.1266/ggs.15-00011. Epub 2015 Nov 26. Genes Genet Syst. 2016. PMID: 26617076 Review.
Cited by
-
The plant-specific DDR factor SOG1 increases chromatin mobility in response to DNA damage.EMBO Rep. 2022 Dec 6;23(12):e54736. doi: 10.15252/embr.202254736. Epub 2022 Oct 24. EMBO Rep. 2022. PMID: 36278395 Free PMC article.
-
Ameliorating effect of nanoparticles and seeds' heat pre-treatment on soybean plants exposed to sea water salinity.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 23;9(11):e21446. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21446. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37964846 Free PMC article.
-
Exogenous application of 5-azacitidin, royal jelly and folic acid regulate plant redox state, expression level of DNA methyltransferases and alleviate adverse effects of salinity stress on Vicia faba L. plants.Heliyon. 2024 May 11;10(10):e30934. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30934. eCollection 2024 May 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38784551 Free PMC article.
-
Plant CDKs-Driving the Cell Cycle through Climate Change.Plants (Basel). 2021 Aug 30;10(9):1804. doi: 10.3390/plants10091804. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34579337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ATM and ATR, two central players of the DNA damage response, are involved in the induction of systemic acquired resistance by extracellular DNA, but not the plant wound response.Front Immunol. 2023 May 15;14:1175786. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1175786. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37256140 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

