COVID-19 and stem cell transplantation; results from an EBMT and GETH multicenter prospective survey
- PMID: 34079042
- PMCID: PMC8171362
- DOI: 10.1038/s41375-021-01302-5
COVID-19 and stem cell transplantation; results from an EBMT and GETH multicenter prospective survey
Abstract
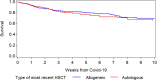
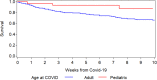
This study reports on 382 COVID-19 patients having undergone allogeneic (n = 236) or autologous (n = 146) hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) reported to the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) or to the Spanish Group of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (GETH). The median age was 54.1 years (1.0-80.3) for allogeneic, and 60.6 years (7.7-81.6) for autologous HCT patients. The median time from HCT to COVID-19 was 15.8 months (0.2-292.7) in allogeneic and 24.6 months (-0.9 to 350.3) in autologous recipients. 83.5% developed lower respiratory tract disease and 22.5% were admitted to an ICU. Overall survival at 6 weeks from diagnosis was 77.9% and 72.1% in allogeneic and autologous recipients, respectively. Children had a survival of 93.4%. In multivariate analysis, older age (p = 0.02), need for ICU (p < 0.0001) and moderate/high immunodeficiency index (p = 0.04) increased the risk while better performance status (p = 0.001) decreased the risk for mortality. Other factors such as underlying diagnosis, time from HCT, GVHD, or ongoing immunosuppression did not significantly impact overall survival. We conclude that HCT patients are at high risk of developing LRTD, require admission to ICU, and have increased mortality in COVID-19.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ljungman P, Mikulska M, de la Camara R, Basak GW, Chabannon C, Corbacioglu S, et al. The challenge of COVID-19 and hematopoietic cell transplantation; EBMT recommendations for management of hematopoietic cell transplant recipients, their donors, and patients undergoing CAR T-cell therapy. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2020;55:2071–6. doi: 10.1038/s41409-020-0919-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed