Counting mitoses: SI(ze) matters!
- PMID: 34079071
- PMCID: PMC8376633
- DOI: 10.1038/s41379-021-00825-7
Counting mitoses: SI(ze) matters!
Abstract
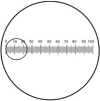
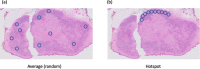
Mitoses are often assessed by pathologists to assist the diagnosis of cancer, and to grade malignancy, informing prognosis. Historically, this has been done by expressing the number of mitoses per n high power fields (HPFs), ignoring the fact that microscope fields may differ substantially, even at the same high power (×400) magnification. Despite a requirement to define HPF size in scientific papers, many authors fail to address this issue adequately. The problem is compounded by the switch to digital pathology systems, where ×400 equivalent fields are rectangular and also vary in the area displayed. The potential for error is considerable, and at times this may affect patient care. This is easily solved by the use of standardized international (SI) units. We, therefore, recommend that features such as mitoses are always counted per mm2, with an indication of the area to be counted and the method used (usually "hotspot" or "average") to obtain the results.
© 2021. World Health Organization.
Conflict of interest statement
RAS is supported by a Commonwealth Government of Australia National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia (NHMRC) Practitioner Fellowship.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

