Base editing of haematopoietic stem cells rescues sickle cell disease in mice
- PMID: 34079130
- PMCID: PMC8266759
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-03609-w
Base editing of haematopoietic stem cells rescues sickle cell disease in mice
Abstract
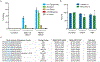
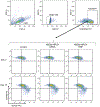
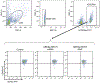
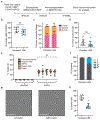
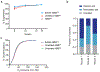
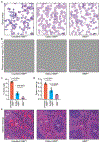
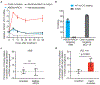
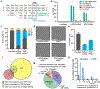
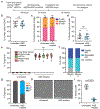
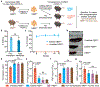
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is caused by a mutation in the β-globin gene HBB1. We used a custom adenine base editor (ABE8e-NRCH)2,3 to convert the SCD allele (HBBS) into Makassar β-globin (HBBG), a non-pathogenic variant4,5. Ex vivo delivery of mRNA encoding the base editor with a targeting guide RNA into haematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) from patients with SCD resulted in 80% conversion of HBBS to HBBG. Sixteen weeks after transplantation of edited human HSPCs into immunodeficient mice, the frequency of HBBG was 68% and hypoxia-induced sickling of bone marrow reticulocytes had decreased fivefold, indicating durable gene editing. To assess the physiological effects of HBBS base editing, we delivered ABE8e-NRCH and guide RNA into HSPCs from a humanized SCD mouse6 and then transplanted these cells into irradiated mice. After sixteen weeks, Makassar β-globin represented 79% of β-globin protein in blood, and hypoxia-induced sickling was reduced threefold. Mice that received base-edited HSPCs showed near-normal haematological parameters and reduced splenic pathology compared to mice that received unedited cells. Secondary transplantation of edited bone marrow confirmed that the gene editing was durable in long-term haematopoietic stem cells and showed that HBBS-to-HBBG editing of 20% or more is sufficient for phenotypic rescue. Base editing of human HSPCs avoided the p53 activation and larger deletions that have been observed following Cas9 nuclease treatment. These findings point towards a one-time autologous treatment for SCD that eliminates pathogenic HBBS, generates benign HBBG, and minimizes the undesired consequences of double-strand DNA breaks.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
Authors have filed patent applications on base editing through the Broad Institute. D.R.L. is a consultant and equity owner of Beam Therapeutics, Prime Medicine, and Pairwise Plants, companies that use genome editing. M.J.W. is on advisory boards for Cellarity Inc., Novartis, and Forma Therapeutics, and is an equity owner of Beam Therapeutics. A.S. is a consultant for Spotlight Therapeutics and his institution receives clinical trial support for the conduct of sickle cell disease gene editing trials from Vertex Pharmaceuticals, CRISPR Therapeutics, and Novartis. J.S.Y is an equity owner of Beam Therapeutics. The authors declare no competing non-financial interests.
Figures




References
-
- Sangkitporn S, Rerkamnuaychoke B, Sangkitporn S, Mitrakul C & Sutivigit Y Hb G Makassar (beta 6:Glu-Ala) in a Thai family. J Med Assoc Thai 85, 577–582 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Blackwell RQ, Oemijati S, Pribadi W, Weng MI & Liu CS Hemoglobin G Makassar: beta-6 Glu leads to Ala. Biochim Biophys Acta 214, 396–401 (1970). - PubMed
References cited in Methods and Extended Data figure legends
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

