Mesenchymal Stem Cells Attenuate Renal Fibrosis via Exosomes-Mediated Delivery of microRNA Let-7i-5p Antagomir
- PMID: 34079249
- PMCID: PMC8164705
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S299969
Mesenchymal Stem Cells Attenuate Renal Fibrosis via Exosomes-Mediated Delivery of microRNA Let-7i-5p Antagomir
Abstract
Background: Renal fibrosis is a chronic and progressive process affecting kidneys in chronic kidney disease (CKD). Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes (MSCs-Exo) have been shown to alleviate renal fibrosis and injury, but the mechanism of MSCs-Exo-induced renal protection remains unknown.
Methods: In this study, MSCs were transfected with let-7i-5p antagomir (anti-let-7i-5p), and then exosomes were isolated from the transfected MSCs to deliver anti-let-7i-5p oligonucleotides to inhibit the level of let-7i-5p in kidney tubular epithelial cells (NRK-52E).
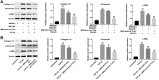
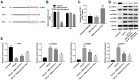
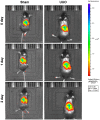
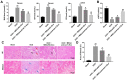
Results: In both NRK-52E cells stimulated by TGF-β1 and the mouse kidneys after unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO), we demonstrated increased level of let-7i-5p. In addition, MSCs-Exo can deliver anti-let-7i-5p to reduce the level of let-7i-5p in NRK-52E cells and increase the expression of its target gene TSC1. Moreover, exosomal anti-let-7i-5p reduced extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition and attenuated epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process in transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1)-stimulated NRK-52E cells and in the kidneys of UUO-treated mice. Meanwhile, mice received exosomal anti-let-7i-5p displayed reduced renal fibrosis and improved kidney function when challenged with UUO. Furthermore, exosomal anti-let-7i-5p promoted the activation the tuberous sclerosis complex subunit 1/mammalian target of rapamycin (TSC1/mTOR) signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro.
Conclusion: In conclusion, exosomal anti-let-7i-5p from MSCs exerts anti-fibrotic effects in TGF-β1-induced fibrogenic responses in NRK52E cells in vitro as well as in UUO-induced renal fibrosis model in vivo. These results provided a novel perspective on improving renal fibrosis by MSCs-Exo.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; exosomes and microRNAs; mesenchymal stem cells; renal fibrosis.
© 2021 Jin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Juan Jin and Fengmei Qian should be considered as co-first authors. The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate renal fibrosis via delivery of miR-186-5p.Hum Cell. 2022 Jan;35(1):83-97. doi: 10.1007/s13577-021-00617-w. Epub 2021 Sep 28. Hum Cell. 2022. PMID: 34585365
-
Exosomal miR-21 from tubular cells contributes to renal fibrosis by activating fibroblasts via targeting PTEN in obstructed kidneys.Theranostics. 2021 Aug 2;11(18):8660-8673. doi: 10.7150/thno.62820. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 34522205 Free PMC article.
-
The Smad3-dependent microRNA let-7i-5p promoted renal fibrosis in mice with unilateral ureteral obstruction.Front Physiol. 2022 Aug 25;13:937878. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.937878. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36091385 Free PMC article.
-
Stem cell-derived and circulating exosomal microRNAs as new potential tools for diabetic nephropathy management.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Jan 24;13(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02696-w. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35073973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic potential: The role of mesenchymal stem cells from diverse sources and their derived exosomes in diabetic nephropathy.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Jun;175:116672. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116672. Epub 2024 Apr 26. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38677249 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of Cell Therapies for Renal Disease and Regenerative Medicine.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 15;23(24):15943. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415943. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Let-7i: A key player and a promising biomarker in diseases.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 Jun 28;48(6):909-919. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2023.220146. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 37587077 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Engineered Extracellular Vesicles in Chronic Kidney Diseases: A Comprehensive Review.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Mar 7;19:2377-2393. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S452393. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38469058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Naïve or Engineered Extracellular Vesicles from Different Cell Sources: Therapeutic Tools for Kidney Diseases.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jun 12;15(6):1715. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15061715. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37376163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Meta-analysis study of the therapeutic impact of Mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes for chronic kidney diseases.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025 Jun 3;43:102072. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2025.102072. eCollection 2025 Sep. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025. PMID: 40524833 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

