CD24 Contributes to Treatment Effect in ABC-DLBCL Patients with R-CHOP Resistance
- PMID: 34079334
- PMCID: PMC8165940
- DOI: 10.2147/PGPM.S310816
CD24 Contributes to Treatment Effect in ABC-DLBCL Patients with R-CHOP Resistance
Abstract
Purpose: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and of which the prognosis of activated B-cell-like (ABC) subtype is poor. Although R-CHOP significantly improves the survival of patients with DLBCL, 20% to 40% of patients were resistant to R-CHOP therapy. Thus, screening for candidate therapeutic targets for R-CHOP resistant patients is urgent. The previous researches have shown that CD24 is related to the development, invasion, and metastasis of cancer. Our project aims to clarify the relationship between CD24 and ABC-DLBCL.
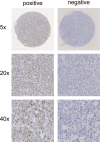
Patients and methods: The expression of CD24 mRNA in 118 ABC-DLBCL cases treated with R-CHOP was detected by RNAscope, and the relationship between CD24 expression and R-CHOP treatment response was analyzed. The correlation between CD24 expression and treatment efficiency was further analyzed by data downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. The association between CD24 expression and immune response was conducted using Cell-type Identification By Estimating Relative Subsets Of RNA Transcripts (CIBERSORT) methodology and Gene Ontology (GO) biological process (BP) analysis.
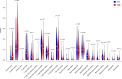
Results: The positive expression rate of CD24 mRNA in ABC-DLBCL patients was 38.1% (45/118). Complete Response (CR) rate was significantly higher in patients with CD24 high expression than those with CD24 low expression (P=0.039; 44.4% vs 26.0%). CR rate was significantly different between CD24 high and low expression groups in the analysis of GEO datasets (P=0.003; 83.2% vs 58.0%). The CD24 high expression patients had significantly lower proportions of T cells and nonspecific immune cells in the CIBERSORT analysis. In addition, T-helper 2 cell differentiation and monocyte chemotaxis were repressed in CD24 high expression group in the GO BP analysis.
Conclusion: CD24 was correlated with better R-CHOP treatment response and tumor immunosuppression in ABC-DLBCL. CD24 may be a promising signal in treatment and prognosis evaluation in ABC-DLBCL patients.
Keywords: ABC-DLBCL; CD24; RNA in situ hybridization; treatment response; tumor immunosuppression.
© 2021 Qiao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

