Environmental Pollution and Peripheral Artery Disease
- PMID: 34079405
- PMCID: PMC8166356
- DOI: 10.2147/RMHP.S307150
Environmental Pollution and Peripheral Artery Disease
Abstract
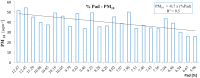
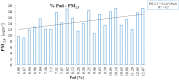
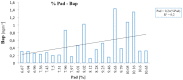
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) of the lower limbs represents one of the most important clinical conditions among vascular disease and can negatively impact quality of life of affected patients, representing also an important socioeconomic burden. Several risk factors predispose to PAD and its complications. Nevertheless, the role of pollution in this context has not been fully evaluated and this article explored the most updated information on epidemiology and environmental pollution in order to hypothesize the possible contribution of air pollution in the onset of PAD. Pollution is an important problem for the global community and has harmful effects on human health and cardiovascular system, and, specifically, particulate matter 10 (PM10) was found significantly associated with PAD.
Keywords: PM10; environment; peripheral artery disease; pollution; risk factors.
© 2021 Serra et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors reported no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures
References
-
- Song P, Rudan D, Zhu Y, et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence and risk factors for peripheral artery disease in 2015: an updated systematic review and analysis. Lancet. 2019;7(8):e1020–e1030. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources