Dexmedetomidine Mitigated NLRP3-Mediated Neuroinflammation via the Ubiquitin-Autophagy Pathway to Improve Perioperative Neurocognitive Disorder in Mice
- PMID: 34079457
- PMCID: PMC8165564
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.646265
Dexmedetomidine Mitigated NLRP3-Mediated Neuroinflammation via the Ubiquitin-Autophagy Pathway to Improve Perioperative Neurocognitive Disorder in Mice
Abstract
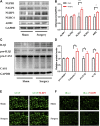
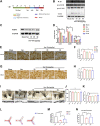
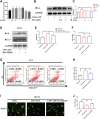
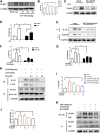
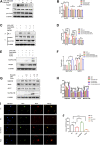
Background: Surgery and anesthesia-induced perioperative neurocognitive disorder (PND) are closely related to NOD-like receptors (NLR) family, pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome microglia inflammatory response. Inhibiting the occurrence of neuroinflammation is an important treatment method to improve postoperative delirium. Fewer NLRP3-targeting molecules are currently available in the clinic to reduce the incidence of postoperative delirium. Dexmedetomidine (DEX), an α2 adrenergic receptor agonist has been shown to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. The present study showed that DEX reduced the production of cleaved caspase1 (CASP1) and destroyed the NLRP3-PYD And CARD Domain Containing (PYCARD)-CASP1 complex assembly, thereby reducing the secretion of IL-1β interleukin beta (IL-1β). DEX promoted the autophagy process of microglia and reduced NLRP3 expression. More interestingly, it promoted the ubiquitination and degradation of NLRP3. Thus, this study demonstrated that DEX reduced NLRP3-mediated inflammation through the activation of the ubiquitin-autophagy pathway. This study provided a new mechanism for treating PND using DEX. Methods: C57BL/6 mice were pre-administered DEX 3 days in advance, and an abdominal exploration model was used to establish a perioperative neurocognitive disorder model. The anti-inflammatory effect of DEX was explored in vivo by detecting NLRP3-CASP1/IL-1β protein expression and behavioral testing. Primary microglia were stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in vitro, the expression of CASP1 and IL-1β was detected in the supernatant of cells, and the expression of autophagy-related proteins microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 beta (MAP1LC3B) and sequestosome 1 (SQSTM1) was examined in the cytoplasm. Meanwhile, Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) was used to detect NLRP3 protein ubiquitination so as to clarify the new mechanism underlying the anti-inflammatory effect of DEX. Results: Pre-administration of DEX reduced the protein expression of NLRP3, CASP1, and IL-1β in the hippocampus of mice induced by surgery and also improved the impairment of learning and memory ability. At the same time, DEX also effectively relieved the decrease in spine density of the hippocampal brain induced by surgery. DEX decreased the cleaved CASP1 expression, blocked the assembly of NLRP3-PYCARD-CASP1 complex, and also reduced the secretion of mature IL-1β in vitro. Mechanically, it accelerated the degradation of NLRP3 inflammasome via the autophagy-ubiquitin pathway and reduced the green fluorescent protein/red fluorescent protein MAP1LC3B ratio, which was comparable to the effect when using the autophagy activator rapamycin (Rapa). Furthermore, it increased the ubiquitination of NLRP3 after LPS plus ATP stimulated microglia. Conclusion: DEX attenuated the hippocampal brain inflammation by promoting NLRP3 inflammasome degradation via the autophagy-ubiquitin pathway, thus improving cognitive impairment in mice.
Keywords: NLRP3 inflammasome; dexmedetomidine; microglial; neuroinflammation; perioperative neurocognitive disorder.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, Xiao, Zhang, Wang, Ying, Wei, Chen, Huang, Yu, Liu, Zheng, Xu, Yu and Hua.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Small molecule-driven NLRP3 inflammation inhibition via interplay between ubiquitination and autophagy: implications for Parkinson disease.Autophagy. 2019 Nov;15(11):1860-1881. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1596481. Epub 2019 Apr 9. Autophagy. 2019. PMID: 30966861 Free PMC article.
-
Actions of dexmedetomidine in regulating NLRP3 in postoperative cognitive dysfunction in aged mice via the autophagy-lysosome pathway.Br J Pharmacol. 2025 Apr;182(8):1683-1703. doi: 10.1111/bph.17378. Epub 2025 Jan 15. Br J Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39815423
-
HIV-1 Tat Primes and Activates Microglial NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Neuroinflammation.J Neurosci. 2017 Mar 29;37(13):3599-3609. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3045-16.2017. Epub 2017 Mar 7. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28270571 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction between autophagy and neuroinflammation in major depressive disorder: From pathophysiology to therapeutic implications.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Jun;168:105586. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105586. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 33812005 Review.
-
The role of autophagy in the regulation of neuroinflammation in acute ischemic stroke (review of literature).Klin Lab Diagn. 2022 Jul 18;67(7):391-398. doi: 10.51620/0869-2084-2022-67-7-391-398. Klin Lab Diagn. 2022. PMID: 35924769 Review. English.
Cited by
-
CB2R Activation Regulates TFEB-Mediated Autophagy and Affects Lipid Metabolism and Inflammation of Astrocytes in POCD.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 22;13:836494. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.836494. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35392078 Free PMC article.
-
β-arrestin1 regulates astrocytic reactivity via Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fission: implications in postoperative delirium.J Neuroinflammation. 2023 May 11;20(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02794-x. J Neuroinflammation. 2023. PMID: 37170230 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicle MicroRNAs as Predictive Biomarkers in Postoperative Delirium After Spine Surgery: Preliminary Study.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2024 Nov 1;79(11):glae162. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glae162. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38970345 Free PMC article.
-
Update of the European Society of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care Medicine evidence-based and consensus-based guideline on postoperative delirium in adult patients.Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2024 Feb 1;41(2):81-108. doi: 10.1097/EJA.0000000000001876. Epub 2023 Aug 30. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2024. PMID: 37599617 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between preoperative high arterial blood lactate level and delirium after deep brain stimulation surgery in Parkinson's disease.Front Aging. 2025 Mar 25;6:1538012. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2025.1538012. eCollection 2025. Front Aging. 2025. PMID: 40201747 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amdur R. L., Feldman H. I., Dominic E. A., Anderson A. H., Beddhu S., Rahman M., et al. (2019). Use of Measures of Inflammation and Kidney Function for Prediction of Atherosclerotic Vascular Disease Events and Death in Patients with CKD: Findings from the CRIC Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 73, 344–353. 10.1053/j.ajkd.2018.09.012 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

