COVID-19 in People With Schizophrenia: Potential Mechanisms Linking Schizophrenia to Poor Prognosis
- PMID: 34079487
- PMCID: PMC8166317
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.666067
COVID-19 in People With Schizophrenia: Potential Mechanisms Linking Schizophrenia to Poor Prognosis
Abstract
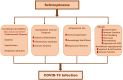
As the global burden of mortality from COVID-19 continues to rise, an understanding of who is most at risk of adverse outcomes is of paramount importance. Pre-existing cardiometabolic, renal and respiratory diseases as well as old age are well-established risk factors associated with disease severity and mortality among patients with COVID-19. However, mounting evidence also indicates an increased susceptibility to, and risk of adverse outcomes from COVID-19 in people with schizophrenia, independent of age and comorbidity. Therefore, elucidating the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms which may increase the risk of poor outcomes in people with schizophrenia is of crucial importance. Here, we provide a narrative on the current understanding of COVID-19 in patients with schizophrenia and propose potential mechanisms which may link schizophrenia with an increased susceptibility to, and greater risk of adverse outcomes from COVID-19. Given the existing knowledge gaps, robust clinical and biological studies are required to further our understanding of some of these underlying mechanisms, so that effective prevention and treatment strategies for COVID-19 in patients with schizophrenia can be developed.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; first episode psychosis; psychosis; schizophrenia; severe mental illness.
Copyright © 2021 Mohan, Perry, Saravanan and Singh.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Healthmap . Novel coronavirus (COVID-19). Boston: Computational Epidemiology Group. Available online at: https://www.healthmap.org/covid-19/ (accessed March 30, 2021).
-
- Correll CU, Solmi M, Veronese N, Bortolato B, Rosson S, Santonastaso P, et al. . Prevalence, incidence and mortality from cardiovascular disease in patients with pooled and specific severe mental illness: a large-scale meta-analysis of 3,211,768 patients and 113,383,368 controls. World Psychiatry. (2017) 16:163–80. 10.1002/wps.20420 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous