Transcranial Doppler Combined With Quantitative Electroencephalography Brain Function Monitoring for Estimating the Prognosis of Patients With Posterior Circulation Cerebral Infarction
- PMID: 34079507
- PMCID: PMC8165540
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2021.600985
Transcranial Doppler Combined With Quantitative Electroencephalography Brain Function Monitoring for Estimating the Prognosis of Patients With Posterior Circulation Cerebral Infarction
Abstract
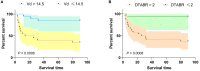
Posterior circulation cerebral infarction (PCCI) can lead to deceased infratentorial cerebral blood flow (CBF) and metabolism. Neural activity is closely related to regional cerebral blood flow both spatially and temporally. Transcranial Doppler (TCD) combined with quantitative electroencephalography (QEEG) is a technique that evaluates neurovascular coupling and involves synergy between the metabolic and vascular systems. This study aimed to monitor brain function using TCD-QEEG and estimate the efficacy of TCD-QEEG for predicting the prognosis of patients with PCCI. We used a TCD-QEEG recording system to perform quantitative brain function monitoring; we recorded the related clinical variables simultaneously. The data were analyzed using a Cox proportional hazards regression model. Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was used to evaluate the cut-off for the diastolic flow velocity (VD) and (delta + theta)/(alpha + beta) ratio (DTABR). The area under the ROC curve (AUROC) was calculated to assess the predictive validity of the study variables. Forty patients (aged 63.7 ± 9.9 years; 30 men) were assessed. Mortality at 90 days was 40%. The TCD indicators of VD [hazard ratio (HR) 0.168, confidence interval (CI) 0.047-0.597, p = 0.006] and QEEG indicators of DTABR (HR 12.527, CI 1.637-95.846, p = 0.015) were the independent predictors of the clinical outcomes. The AUROC after combination of VD and DTABR was 0.896 and showed better predictive accuracy than the Glasgow Coma Scale score (0.75), VD (0.76), and DTABR (0.781; all p < 0.05). TCD-QEEG provides a good understanding of the coupling mechanisms in the brain and can improve our ability to predict the prognosis of patients with PCCI.
Keywords: brain function monitoring; cerebral infarction; prognosis; quantitative electroencephalography; transcranial Doppler.
Copyright © 2021 Cao, Song, Wang, Qi, Chen and Xing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transcranial Doppler combined with quantitative EEG brain function monitoring and outcome prediction in patients with severe acute intracerebral hemorrhage.Crit Care. 2018 Feb 20;22(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s13054-018-1951-y. Crit Care. 2018. PMID: 29463290 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal Monitoring in Large Hemispheric Infarction: Quantitative Electroencephalography Combined With Transcranial Doppler for Prognosis Prediction.Front Neurol. 2021 Dec 8;12:724571. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.724571. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34956039 Free PMC article.
-
Monitoring of patients with brainstem hemorrhage: A simultaneous study of quantitative electroencephalography and transcranial Doppler.Clin Neurophysiol. 2021 Apr;132(4):946-952. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2020.12.026. Epub 2021 Feb 5. Clin Neurophysiol. 2021. PMID: 33636610
-
Transcranial Doppler ultrasonography in neurological surgery and neurocritical care.Neurosurg Focus. 2019 Dec 1;47(6):E2. doi: 10.3171/2019.9.FOCUS19611. Neurosurg Focus. 2019. PMID: 31786564 Review.
-
Non-invasive brain stimulation in the modulation of cerebral blood flow after stroke: A systematic review of Transcranial Doppler studies.Clin Neurophysiol. 2018 Dec;129(12):2544-2551. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2018.09.019. Epub 2018 Oct 25. Clin Neurophysiol. 2018. PMID: 30384025
Cited by
-
Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Image Combined with Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Patients with Cerebral Infarction and Vertigo.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022 Jun 30;2022:5313238. doi: 10.1155/2022/5313238. eCollection 2022. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35833063 Free PMC article.
-
Laser speckle contrast imaging for blood flow monitoring in predicting outcomes after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice.BMC Neurosci. 2022 Dec 27;23(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s12868-022-00769-x. BMC Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36575381 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

