A Rare Case of Brain Abscesses Caused by Acremonium Species
- PMID: 34079648
- PMCID: PMC8159309
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.14396
A Rare Case of Brain Abscesses Caused by Acremonium Species
Abstract
Acremonium species are saprophytic fungi that are rarely pathogenic in humans. According to several reports, Acremonium species can cause various diseases, ranging from superficial infections after traumatic inoculation in immunocompetent individuals to invasive infections in the immunocompromised. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case report of brain abscess in an 18-year-old male caused by Acremonium species in Pakistan. A combination of intravenous amphotericin B and oral voriconazole was administered to the patient, which resulted in marked clinical improvement. However, the recurrence of fungiwas observed after three months of completion of the antifungal course. The purpose of this report is to alert clinicians regarding this pathogen and its ability to cause systemic disease.
Keywords: acremonium; amphotericin; brain abscess; fungal abscess; recurrence; voriconazole.
Copyright © 2021, Anis et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
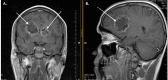
Figures


Similar articles
-
Fungal brain abscesses caused by Acremonium species.Egypt J Intern Med. 2023;35(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s43162-022-00183-z. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Egypt J Intern Med. 2023. PMID: 36741047 Free PMC article.
-
Acremonium species associated fungemia: a novel pathogen in the immunosuppressed patient.Bol Asoc Med P R. 2014;106(3):29-31. Bol Asoc Med P R. 2014. PMID: 25470906
-
A novel fungal pathogen under the spotlight--Acremonium spp. associated fungaemia in an immunocompetent host.Mycoses. 2011 Jan;54(1):78-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.2009.01762.x. Mycoses. 2011. PMID: 19702621
-
Multiple Brain Abscesses Due to Phialemonium in a Renal Transplant Recipient: First Case Report in the Literature.Exp Clin Transplant. 2015 Nov;13 Suppl 3:77-80. doi: 10.6002/ect.tdtd2015.P31. Exp Clin Transplant. 2015. PMID: 26640919 Review.
-
Sarocladium and Acremonium infections: New faces of an old opportunistic fungus.Mycoses. 2020 Nov;63(11):1203-1214. doi: 10.1111/myc.13169. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Mycoses. 2020. PMID: 33090564 Review.
Cited by
-
Fungal footprints in oral cancer: unveiling the oral mycobiome.Front Oral Health. 2024 Mar 14;5:1360340. doi: 10.3389/froh.2024.1360340. eCollection 2024. Front Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 38550775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fungal brain abscesses caused by Acremonium species.Egypt J Intern Med. 2023;35(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s43162-022-00183-z. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Egypt J Intern Med. 2023. PMID: 36741047 Free PMC article.
-
Morphological characteristics and phylogenetic evidence reveal two new species of Acremonium (Hypocreales, Sordariomycetes).MycoKeys. 2022 Jul 15;91:85-96. doi: 10.3897/mycokeys.91.86257. eCollection 2022. MycoKeys. 2022. PMID: 36760887 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acremonium species: a review of the etiological agents of emerging hyalohyphomycosis. Das S, Saha R, Dar SA, Ramachandran VG. Mycopathologia. 2010;170:361–375. - PubMed
-
- Infection due to the fungus Acremonium (cephalosporium) Fincher RM, Fisher JF, Lovell RD, Newman CL, Espinel-Ingroff A, Shadomy HJ. Medicine (Baltimore) 1991;70:398–409. - PubMed
-
- A review on emerging fungal infections and their significance. Kant R, Kaur T, Gupte S, Kaur M. J Bacteriol Mycol. 2015;1:39–41.
-
- Emerging fungi. Nucci M, Anaissie E. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2006;20:563–579. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
