Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review of Primary Renal Tubular Acidosis in Patients With Autoimmune Hepatitis and Alcoholic Hepatitis
- PMID: 34079685
- PMCID: PMC8161551
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.15287
Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review of Primary Renal Tubular Acidosis in Patients With Autoimmune Hepatitis and Alcoholic Hepatitis
Abstract
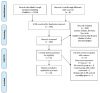
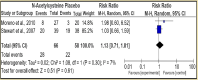
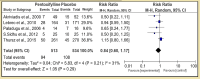
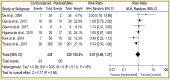
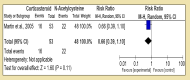
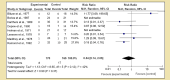
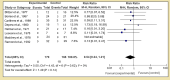
Renal and hepatic functions are often mingled through both the existence of associated primary organ diseases and hemodynamic co-relationship. The primary objective of this study was to sum up the relationship between autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) on renal tubular acidosis (RTA) and the stages of the disease. A systematic review was performed for 24 trials. A total of 3687 patients were included. The incidence of RTA occurring and short-term mortality reduction was seen in two groups; for an overall effect: Z = 2.85 (P = 0.004) a total 95% CI of 0.53 [0.34, 0.82]. Only one patient with alcoholic liver cirrhosis was found to have an incomplete type of RTA. Test for overall effect: Z = 2.28 (P = 0.02) 95% CI of 2.83 [1.16, 6.95]. A reduction in fatal infections with dual therapy of corticosteroid plus N-acetylcysteine (NAC) test for overall effect: Z = 3.07 (P = 0.002) with 95% CI of 0.45 [0.27, 0.75]. Autoimmune diseases are the most frequent underlying cause of secondary RTA in adults. The primary renal disease must be actively excluded in all patients with hepatic failure by aggressive clinical and laboratory evaluations.
Keywords: autoimmune hepatitis; end-stage liver disease; liver cirrhosis; renal failure; renal tubular acidosis.
Copyright © 2021, Gadour et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Autoimmune Hepatitis with Distal Renal Tubular Acidosis and Small Bowel Partial Malrotation.Euroasian J Hepatogastroenterol. 2015 Jul-Dec;5(2):107-109. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10018-1145. Epub 2016 Jul 9. Euroasian J Hepatogastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 29201703 Free PMC article.
-
Distal renal tubular acidosis in hepatic cirrhosis: clinical and pathogenetic study.Clin Nephrol. 1981 Mar;15(3):143-7. Clin Nephrol. 1981. PMID: 7273489
-
Clinical and laboratory approaches in the diagnosis of renal tubular acidosis.Pediatr Nephrol. 2015 Dec;30(12):2099-107. doi: 10.1007/s00467-015-3083-9. Epub 2015 Apr 1. Pediatr Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25823989 Review.
-
[Clinical and pathological characteristics and outcome of 46 children with autoimmune hepatitis].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2019 Jan 2;57(1):40-45. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1310.2019.01.010. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 30630230 Chinese.
-
Might distal renal tubular acidosis be a proximal tubular cell disorder?Am J Kidney Dis. 1992 Mar;19(3):272-81. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(13)80009-1. Am J Kidney Dis. 1992. PMID: 1553972 Review.
Cited by
-
Current Medical Treatment for Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2022 Sep-Oct;12(5):1333-1348. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2022.02.001. Epub 2022 Feb 12. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 36157148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current and emerging therapies for alcohol-associated hepatitis.Liver Res. 2023 Mar 15;7(1):35-46. doi: 10.1016/j.livres.2023.03.002. eCollection 2023 Mar. Liver Res. 2023. PMID: 39959695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distal Renal Tubular Acidosis in Patients with Autoimmune Diseases-An Update on Pathogenesis, Clinical Presentation and Therapeutic Strategies.Biomedicines. 2022 Aug 31;10(9):2131. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10092131. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36140232 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Increased intestinal permeability to macromolecules and endotoxemia in patients with chronic alcohol abuse in different stages of alcohol-induced liver disease. Parlesak A, Schäfer C, Schütz T, Bode JC, Bode C. J Hepatol. 2000;32:742–747. - PubMed
-
- Oxidative mechanisms in the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease. Albano E. Mol Aspects Med. 2008;29:9–16. - PubMed
-
- Cholestasis and alcoholic liver disease. Tung BY, Carithers RL Jr. Clin Liver Dis. 1999;3:585–601. - PubMed
-
- Apoptosis and alcoholic liver disease. Nanji AA. Semin Liver Dis. 1998;18:187–190. - PubMed
-
- Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of alcoholic liver disease. Menon KV, Gores GJ, Shah VH. Mayo Clin Proc. 2001;76:1021–1029. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
