Association between population vitamin D status and SARS-CoV-2 related serious-critical illness and deaths: An ecological integrative approach
- PMID: 34079693
- PMCID: PMC8152454
- DOI: 10.5501/wjv.v10.i3.111
Association between population vitamin D status and SARS-CoV-2 related serious-critical illness and deaths: An ecological integrative approach
Abstract
Background: Vitamin D population status may have possible unappreciated consequences to the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. Α significant association between vitamin D sufficiency and reduction in clinical severity and inpatient mortality from COVID-19 disease has recently been shown, while a recent study has claimed lower COVID-19 cases in European countries with a better vitamin D status. Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin-D [25(OH)D] was identified as an independent risk factor for COVID-19 infection and hospitalization, and administration of 0.532 mg (21280 IU) of calcifediol or 25(OH)D, followed by 0.266 mg on days 3 and 7 and then weekly until discharge or intensive care unit admission significantly reduced the need for intensive care unit treatment.
Aim: To elucidate the role of vitamin D European population status in the COVID-19 pandemic, data from the Worldometer were analyzed.
Methods: Linear regression explored the correlation between published representative-standardized population vitamin D concentrations and the number of total cases/million (M), recovered/M, deaths/M and serious-critically ill/M from COVID-19 for 26 European countries populated > 4 M (Worldometer). Life expectancy was analyzed with semi-parametric regression. Weighted analysis of variance/analysis of covariance evaluated serious-critical/M and deaths/M by the vitamin D population status: Deficient < 50, insufficient: 50-62.5, mildly insufficient > 62.5-75 and sufficient > 75 nmol/L, while controlling for life expectancy for deaths/M. Statistical analyses were performed in XLSTAT LIFE SCIENCE and R (SemiPar Library).
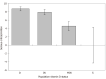
Results: Linear regression found no correlation between population vitamin D concentrations and the total cases-recovered/M, but negative correlations predicting a reduction of 47%-64%-80% in serious-critical illnesses/M and of 61%-82%-102.4% in deaths/M further enhanced when adapting for life expectancy by 133-177-221% if 25(OH)D concentrations reach 100-125-150 nmol/L, sustained on August 15, 2020, indicating a truthful association. Weighted analysis of variance was performed to evaluate serious-critical/M (r 2 = 0.22) by the vitamin D population status and analysis of covariance the deaths/M (r 2 = 0.629) controlling for life expectancy (r 2 = 0.47). Serious-critical showed a decreasing trend (P < 0.001) from population status deficient (P < 0.001) to insufficient by 9.2% (P < 0.001), to mildly insufficient by 47.6% (P < 0.044) and to sufficient by 100% (reference, P < 0.001). For deaths/M the respective decreasing trend (P < 0.001) was 62.9% from deficient (P < 0.001) to insufficient (P < 0.001), 65.15% to mildly insufficient (P < 0.001) and 78.8% to sufficient (P = 0.041).
Conclusion: Achieving serum 25(OH)D 100-150 nmol/L (40-60 ng/mL) (upper tolerable daily doses followed by maintenance proposed doses not requiring medical supervision, Endocrine Society) may protect from serious-critical illness/death from COVID-19 disease.
Keywords: 25-hydroxyvitamin-D; COVID-19; Immunity; SARS-CoV-2; Vitamin D concentrations; Vitamin D status.
©The Author(s) 2021. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Holick MF was a former consultant for Quest Diagnostics, consultant for Ontometrics Inc. and speaker’s Bureau for Abbott Inc. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures




References
-
- Hilger J, Friedel A, Herr R, Rausch T, Roos F, Wahl DA, Pierroz DD, Weber P, Hoffmann K. A systematic review of vitamin D status in populations worldwide. Br J Nutr. 2014;111:23–45. - PubMed
-
- Bolland MJ, Grey A, Avenell A. Effects of vitamin D supplementation on musculoskeletal health: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and trial sequential analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6:847–858. - PubMed
-
- Sempos CT, Heijboer AC, Bikle DD, Bollerslev J, Bouillon R, Brannon PM, DeLuca HF, Jones G, Munns CF, Bilezikian JP, Giustina A, Binkley N. Vitamin D assays and the definition of hypovitaminosis D: results from the First International Conference on Controversies in Vitamin D. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2018;84:2194–2207. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

