Non-invasive detection of intracranial pressure related to the optic nerve
- PMID: 34079745
- PMCID: PMC8107303
- DOI: 10.21037/qims-20-1188
Non-invasive detection of intracranial pressure related to the optic nerve
Abstract
Intracranial pressure (ICP) is associated with a variety of diseases. Early diagnosis and the timely intervention of elevated ICP are effective means to clinically reduce the morbidity and mortality of some diseases. The detection and judgment of reduced ICP are beneficial to glaucoma doctor and neuro ophthalmologist to diagnose optic nerve disease earlier. It is important to evaluate and monitor ICP clinically. Although invasive ICP detection is the gold standard, it can have complications. Most non-invasive ICP tests are related to the optic nerve and surrounding tissues due to their anatomical characteristics. Ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging, transcranial Doppler, papilledema on optical coherence tomography, visual evoked potential, ophthalmodynamometry, the assessment of spontaneous retinal venous pulsations, and eye-tracking have potential for application. Although none of these methods can completely replace invasive technology; however, its repeatable, low risk, high accuracy, gradually attracted people's attention. This review summarizes the non-invasive ICP detection methods related to the optic nerve and the role of the diagnosis and prognosis of neurological disorders and glaucoma. We discuss the advantages and challenges and predict possible areas of development in the future.
Keywords: Intracranial pressure (ICP); magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); optic nerve; transcranial Doppler (TCD); ultrasound.
2021 Quantitative Imaging in Medicine and Surgery. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Both authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/qims-20-1188). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

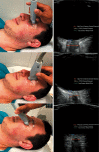
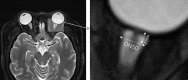
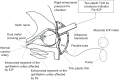
References
-
- Lindén C, Qvarlander S, Jóhannesson G, Johansson E, Östlund F, Malm J, Eklund A. Normal-Tension Glaucoma Has Normal Intracranial Pressure: A Prospective Study of Intracranial Pressure and Intraocular Pressure in Different Body Positions. Ophthalmology 2018;125:361-8. 10.1016/j.ophtha.2017.09.022 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen CL, Bojikian KD, Gupta D, Wen JC, Zhang Q, Xin C, Kono R, Mudumbai RC, Johnstone MA, Chen PP, Wang RK. Optic nerve head perfusion in normal eyes and eyes with glaucoma using optical coherence tomography-based microangiography. Quant Imaging Med Surg 2016;6:125-33. 10.21037/qims.2016.03.05 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
