Expert-level classification of gastritis by endoscopy using deep learning: a multicenter diagnostic trial
- PMID: 34079883
- PMCID: PMC8159578
- DOI: 10.1055/a-1372-2789
Expert-level classification of gastritis by endoscopy using deep learning: a multicenter diagnostic trial
Abstract
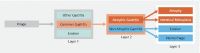
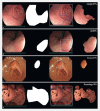
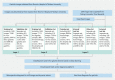
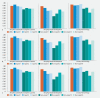
Background and study aims Endoscopy plays a crucial role in diagnosis of gastritis. Endoscopists have low accuracy in diagnosing atrophic gastritis with white-light endoscopy (WLE). High-risk factors (such as atrophic gastritis [AG]) for carcinogenesis demand early detection. Deep learning (DL)-based gastritis classification with WLE rarely has been reported. We built a system for improving the accuracy of diagnosis of AG with WLE to assist with this common gastritis diagnosis and help lessen endoscopist fatigue. Methods We collected a total of 8141 endoscopic images of common gastritis, other gastritis, and non-gastritis in 4587 cases and built a DL -based system constructed with UNet + + and Resnet-50. A system was developed to sort common gastritis images layer by layer: The first layer included non-gastritis/common gastritis/other gastritis, the second layer contained AG/non-atrophic gastritis, and the third layer included atrophy/intestinal metaplasia and erosion/hemorrhage. The convolutional neural networks were tested with three separate test sets. Results Rates of accuracy for classifying non-atrophic gastritis/AG, atrophy/intestinal metaplasia, and erosion/hemorrhage were 88.78 %, 87.40 %, and 93.67 % in internal test set, 91.23 %, 85.81 %, and 92.70 % in the external test set ,and 95.00 %, 92.86 %, and 94.74 % in the video set, respectively. The hit ratio with the segmentation model was 99.29 %. The accuracy for detection of non-gastritis/common gastritis/other gastritis was 93.6 %. Conclusions The system had decent specificity and accuracy in classification of gastritis lesions. DL has great potential in WLE gastritis classification for assisting with achieving accurate diagnoses after endoscopic procedures.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests Drs. Shan Hu, Xiao Hu, and Chao Li are research staff members of Wuhan EndoAngel Medical Technology Company.
Figures
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Correa P. Human Gastric Carcinogenesis: A Multistep and Multifactorial Process—First American Cancer Society Award Lecture on Cancer Epidemiology and Prevention. Cancer Research. 1992;52:6735. - PubMed
-
- Rugge M, Meggio A, Pravadelli C et al. Gastritis staging in the endoscopic follow-up for the secondary prevention of gastric cancer: a 5-year prospective study of 1755 patients. Gut. 2019;68:11–17. - PubMed
-
- Leung W K, Ho H J, Lin J-T et al. Prior gastroscopy and mortality in patients with gastric cancer: a matched retrospective cohort study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018;87:119–1.27E115. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

