Glucosylceramide and galactosylceramide, small glycosphingolipids with significant impact on health and disease
- PMID: 34080016
- PMCID: PMC8684486
- DOI: 10.1093/glycob/cwab046
Glucosylceramide and galactosylceramide, small glycosphingolipids with significant impact on health and disease
Abstract
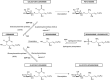
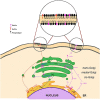
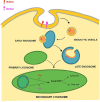
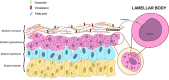
Numerous clinical observations and exploitation of cellular and animal models indicate that glucosylceramide (GlcCer) and galactosylceramide (GalCer) are involved in many physiological and pathological phenomena. In many cases, the biological importance of these monohexosylcermides has been shown indirectly as the result of studies on enzymes involved in their synthesis and degradation. Under physiological conditions, GalCer plays a key role in the maintenance of proper structure and stability of myelin and differentiation of oligodendrocytes. On the other hand, GlcCer is necessary for the proper functions of epidermis. Such an important lysosomal storage disease as Gaucher disease (GD) and a neurodegenerative disorder as Parkinson's disease are characterized by mutations in the GBA1 gene, decreased activity of lysosomal GBA1 glucosylceramidase and accumulation of GlcCer. In contrast, another lysosomal disease, Krabbe disease, is associated with mutations in the GALC gene, resulting in deficiency or decreased activity of lysosomal galactosylceramidase and accumulation of GalCer and galactosylsphingosine. Little is known about the role of both monohexosylceramides in tumor progression; however, numerous studies indicate that GlcCer and GalCer play important roles in the development of multidrug-resistance by cancer cells. It was shown that GlcCer is able to provoke immune reaction and acts as a self-antigen in GD. On the other hand, GalCer was recognized as an important cellular receptor for HIV-1. Altogether, these two molecules are excellent examples of how slight differences in chemical composition and molecular conformation contribute to profound differences in their physicochemical properties and biological functions.
Keywords: biological functions; galactosylceramide; glucosylceramide; glycosphingolipids; neurological diseases.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phosphatidylcholine synthesis is elevated in neuronal models of Gaucher disease due to direct activation of CTP:phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase by glucosylceramide.FASEB J. 2002 Nov;16(13):1814-6. doi: 10.1096/fj.02-0149fje. Epub 2002 Sep 5. FASEB J. 2002. PMID: 12223447
-
Neuronal accumulation of glucosylceramide in a mouse model of neuronopathic Gaucher disease leads to neurodegeneration.Hum Mol Genet. 2014 Feb 15;23(4):843-54. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt468. Epub 2013 Sep 24. Hum Mol Genet. 2014. PMID: 24064337 Free PMC article.
-
Lysosomal membrane integrity in fibroblasts derived from patients with Gaucher disease.Cell Struct Funct. 2024 Jan 23;49(1):1-10. doi: 10.1247/csf.23066. Epub 2023 Dec 9. Cell Struct Funct. 2024. PMID: 38072450 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal forms of Gaucher disease.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2013;(216):405-19. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-1511-4_20. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23563668 Review.
-
The metabolism of glucocerebrosides - From 1965 to the present.Mol Genet Metab. 2017 Jan-Feb;120(1-2):22-26. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2016.11.390. Epub 2016 Dec 2. Mol Genet Metab. 2017. PMID: 27955980 Review.
Cited by
-
A proteogenomic view of Parkinson's disease causality and heterogeneity.NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2023 Feb 11;9(1):24. doi: 10.1038/s41531-023-00461-9. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2023. PMID: 36774388 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand Activation of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Upregulates Epidermal Uridine Diphosphate Glucose Ceramide Glucosyltransferase and Glucosylceramides.J Invest Dermatol. 2023 Oct;143(10):1964-1972.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2023.03.1662. Epub 2023 Mar 31. J Invest Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37004877 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of Spin-Labeled α-/β-Galactosylceramides and Glucosylceramides as Electron Paramagnetic Probes.J Org Chem. 2025 Jan 10;90(1):877-888. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.4c02423. Epub 2024 Dec 16. J Org Chem. 2025. PMID: 39680867 Free PMC article.
-
Determining β-Monosaccharide Head Group Composition with High-Resolution Cyclic Ion Mobility Separations Coupled to Tandem Mass Spectrometry as a First Step for Unknown Cerebroside Analysis.Int J Mass Spectrom. 2025 Aug;514:117459. doi: 10.1016/j.ijms.2025.117459. Epub 2025 Apr 25. Int J Mass Spectrom. 2025. PMID: 40365272
-
Neurodegenerative Disorder Risk in Krabbe Disease Carriers.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 4;23(21):13537. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113537. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362324 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe A, Radin NS, Shayman JA. 1996. Induction of glucosylceramide synthase by synthase inhibitors and ceramide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1299(3):333–341. - PubMed
-
- Abraham W, Wertz PW, Downing DT. 1985. Linoleate-rich acylglucosylceramides of pig epidermis: Structure determination by proton magnetic resonance. J Lipid Res. 26(6):761–766. - PubMed
-
- Albrecht S, Vainauskas S, Stockmann H, McManus C, Taron CH, Rudd PM. 2016. Comprehensive profiling of glycosphingolipid glycans using a novel broad specificity endoglycoceramidase in a high-throughput workflow. Anal Chem. 88(9):4795–4802. - PubMed
-
- Ariga T, Ando S, Takahashi A, Miyatake T. 1980. Gangliosides and neutral glycolipids of human adrenal medulla. Biochim Biophys Acta. 618(3):480–485. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

