Porcupine inhibitor LGK‑974 inhibits Wnt/β‑catenin signaling and modifies tumor‑associated macrophages resulting in inhibition of the malignant behaviors of non‑small cell lung cancer cells
- PMID: 34080032
- PMCID: PMC8185506
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12189
Porcupine inhibitor LGK‑974 inhibits Wnt/β‑catenin signaling and modifies tumor‑associated macrophages resulting in inhibition of the malignant behaviors of non‑small cell lung cancer cells
Abstract
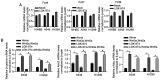
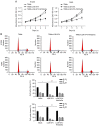
Tumor‑associated macrophages (TAMs) are critical components of the tumor microenvironment that are tightly associated with malignancies in human cancers, including lung cancer. LGK‑974, a small molecular inhibitor of Wnt secretion, was reported to block Wnt/β‑catenin signaling and exert anti‑inflammatory effects by suppressing pro‑inflammatory gene expression in cancer cells. Although it was reported that Wnt/β‑catenin was critical in regulating TAMs, it is still largely unknown whether LGK‑974 regulates tumor malignancies by regulating TAMs. The present study firstly verified that the polarization of TAMs was regulated by LGK‑974. LGK‑974 increased M1 macrophage functional markers and decreased M2 macrophage functional markers. The addition of Wnt3a and Wnt5a, two canonical Wnt signaling inducers, reversed the decrease in M1 macrophage functional markers, including mannose receptor, IL‑10 and Arg1, by activating Wnt/β‑catenin signaling. Conditioned medium from LGK‑974‑modified TAMs inhibited the malignant behaviors in A549 and H1299 cells, including proliferation, colony formation and invasion, by blocking Wnt/β‑catenin signaling. LGK‑974‑modified TAMs blocked the cell cycle at the G1/G0 phase, which was reversed by the addition of Wnt3a/5a, indicating that LGK‑974 regulates the microenvironment by blocking Wnt/β‑catenin signaling. Taken together, the results indicate that LGK‑974 indirectly inhibited the malignant behaviors of A549 and H1299 cells by regulating the inflammatory microenvironment by inhibiting Wnt/β‑catenin signaling in TAMs.
Keywords: LGK‑974; Wnt/β‑catenin signaling; lung cancer; tumor microenvironment; tumor‑associated macrophages.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Porcupine Inhibitor LGK974 Downregulates the Wnt Signaling Pathway and Inhibits Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Feb 13;2020:2527643. doi: 10.1155/2020/2527643. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32104684 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Wnt-driven cancer through the inhibition of Porcupine by LGK974.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Dec 10;110(50):20224-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1314239110. Epub 2013 Nov 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24277854 Free PMC article.
-
LPS-induced inflammatory response is suppressed by Wnt inhibitors, Dickkopf-1 and LGK974.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 27;7:41612. doi: 10.1038/srep41612. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28128299 Free PMC article.
-
Porcupine inhibitors: Novel and emerging anti-cancer therapeutics targeting the Wnt signaling pathway.Pharmacol Res. 2021 May;167:105532. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105532. Epub 2021 Mar 4. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 33677106 Review.
-
Chemical Modulation of WNT Signaling in Cancer.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2018 Jan;153:245-269. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2017.11.008. Epub 2018 Jan 8. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2018. PMID: 29389519 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Biomarkers and Signaling Pathways of Cancer Stem Cells in Colorectal Cancer.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15330338241254061. doi: 10.1177/15330338241254061. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 38794896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The genomic landscape of the immune system in lung cancer: present insights and continuing investigations.Front Genet. 2024 Jun 25;15:1414487. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1414487. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 38983267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oncogenic KRAS Mutations Confer a Unique Mechanotransduction Response to Peristalsis in Colorectal Cancer Cells.Mol Cancer Res. 2025 Feb 6;23(2):128-142. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-24-0624. Mol Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 39485528 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting tumor-associated macrophage: an adjuvant strategy for lung cancer therapy.Front Immunol. 2023 Nov 13;14:1274547. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1274547. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38022518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suppression of tumor cell lactate-generating signaling pathways eradicates murine PTEN/p53-deficient aggressive-variant prostate cancer via macrophage phagocytosis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 May 23:2023.05.23.540590. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.23.540590. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Dec 1;29(23):4930-4940. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-1441. PMID: 37292972 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

