Prognostic value of baseline interleukin 6 levels in liver decompensation and survival in HCC patients undergoing radioembolization
- PMID: 34080071
- PMCID: PMC8172845
- DOI: 10.1186/s13550-021-00791-w
Prognostic value of baseline interleukin 6 levels in liver decompensation and survival in HCC patients undergoing radioembolization
Abstract
Background: To confirm the prognostic value of previously published baseline interleukin 6 (IL6) and IL8 cutoff values in survival and liver dysfunction in patients with advanced HCC undergoing 90Y radioembolization.
Methods: A total of 83 patients (77 male) represented a subset of HCC patients undergoing 90Y radioembolization combined with sorafenib as part of the prospective multicenter phase II trial SORAMIC. IL6 and IL8 levels were determined in serum samples collected at baseline. In this post hoc analysis, we sought to confirm the prognostic value of baseline cutoff values of 6.53 pg/mL and 60.8 pg/mL for IL6 and IL8, respectively, in overall survival (OS) or liver dysfunction (grade 2 bilirubin increase) after treatment.
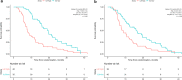
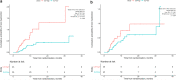
Results: Median OS was 12.0 months. While low baseline albumin and high bilirubin values were associated with high IL6, liver cirrhosis, alcoholic liver disease, and portal vein infiltration were associated with high IL8. In univariate analysis, high baseline IL6 and IL8 were associated with significantly shorter overall survival (7.8 vs. 19.0 months for IL6 and 8.4 vs. 16.0 months for IL8). In addition to IL values, liver cirrhosis, Child-Pugh grade, baseline albumin (< 36 g/dL), and total bilirubin (≥ 17 µmol/L), and higher mALBI grade (2b &3) values were associated with OS. At multivariate analysis, high baseline IL6 was the only independent prognostic factor for OS (HR 2.35 [1.35-4.1], p = 0.002). Risk factors for liver dysfunction were high baseline IL6, albumin, and total bilirubin, and mALBI grade as found in univariate analysis. High baseline IL6 (HR 2.67 [1.21-5.94], p = 0.016) and total bilirubin ≥ 17 µmol/L (HR 3.73 [1.72-8.06], p < 0.001) were independently associated with liver dysfunction.
Conclusion: In advanced HCC patients receiving 90Y radioembolization combined with sorafenib, baseline IL6 values proved to be prognostic, confirming previous findings in patients undergoing 90Yradioembolization. IL6 might be useful for patient selection or stratification in future trials.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Interleukin; Liver decompensation; Radioembolization; Survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Holger Amthauer: Grants: Sirtex, Bayer. Personal fees: Sirtex, GE Healthcare, Novartis, outside the submitted work. Kerstin Schütte: Personal fees: Bayer. Peter Malfertheiner: Grants: Bayer, Sirtex. Heinz Josef Klümpen: Grants: Bayer, Personal fees: Ipsen, outside the submitted work. Bruno Sangro: Personal fees: Sirtex, BTG, Bayer, BMS, Astra Zeneca, Eli Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Terumo, Adaptimmune; Non-financial support: Sirtex, BMS, outside the submitted work. Maciej Pech: Grants: Sirtex, Bayer; Personal fees: Sirtex. Peter Bartenstein: Grants: Sirtex. Jens Ricke: Grants: Sirtex, Bayer; Personal fees: Sirtex, Bayer. Max Seidensticker: Personal fees: Bayer, Sirtex.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Baseline Interleukin-6 and -8 predict response and survival in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with sorafenib monotherapy: an exploratory post hoc analysis of the SORAMIC trial.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2022 Feb;148(2):475-485. doi: 10.1007/s00432-021-03627-1. Epub 2021 Apr 14. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 33855585 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
90Y Radioembolization for Locally Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Thrombosis: Long-Term Outcomes in a 185-Patient Cohort.J Nucl Med. 2018 Jul;59(7):1042-1048. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.117.199752. Epub 2017 Dec 7. J Nucl Med. 2018. PMID: 29217739
-
Development of a prognostic score to predict response to Yttrium-90 radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein invasion.J Hepatol. 2018 Apr;68(4):724-732. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.12.026. Epub 2018 Jan 10. J Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 29331342
-
Comparison of Radioembolization and Sorafenib for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Safety and Efficacy.Korean J Radiol. 2019 Mar;20(3):385-398. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.0496. Korean J Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30799569 Free PMC article.
-
Application of the Albumin-Bilirubin Grade in Predicting the Prognosis of Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Transplant Proc. 2019 Dec;51(10):3338-3346. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2019.08.027. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Transplant Proc. 2019. PMID: 31732203
Cited by
-
Liver-Directed Therapy Combined with Systemic Therapy: Current Status and Future Directions.Semin Intervent Radiol. 2024 Jan 24;40(6):515-523. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-1777711. eCollection 2023 Dec. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38274222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating the prognostic impact of inflammatory markers on treatment outcomes in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma undergoing radioembolization.Diagn Interv Radiol. 2025 Jul 8;31(4):377-383. doi: 10.4274/dir.2024.242929. Epub 2024 Nov 25. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39582209 Free PMC article.
-
Friend or Foe? Locoregional Therapies and Immunotherapies in the Current Hepatocellular Treatment Landscape.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 14;24(14):11434. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411434. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of IL-8 on survival after TARE in HCC: a comprehensive investigation and external validation from the SORAMIC trial.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Nov 6;150(11):486. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05947-4. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39503874 Free PMC article.
-
Baseline Interleukin-6 as a Preoperative Biomarker for Liver Fibrosis.Visc Med. 2024 Jan;39(6):184-192. doi: 10.1159/000535627. Epub 2023 Dec 27. Visc Med. 2024. PMID: 38205272 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

