Phytochemical library screening reveals betulinic acid as a novel Skp2-SCF E3 ligase inhibitor in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 34080260
- PMCID: PMC8353894
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.15005
Phytochemical library screening reveals betulinic acid as a novel Skp2-SCF E3 ligase inhibitor in non-small cell lung cancer
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Phytochemical library screening reveals betulinic acid as a novel Skp2-SCF E3 ligase inhibitor in non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Sci. 2024 Jun;115(6):2083-2085. doi: 10.1111/cas.16163. Epub 2024 Mar 20. Cancer Sci. 2024. PMID: 38507574 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
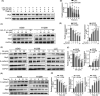
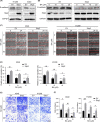
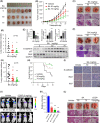
Skp2 is overexpressed in multiple cancers and plays a critical role in tumor development through ubiquitin/proteasome-dependent degradation of its substrate proteins. Drugs targeting Skp2 have exhibited promising anticancer activity. Here, we identified a plant-derived Skp2 inhibitor, betulinic acid (BA), via high-throughput structure-based virtual screening of a phytochemical library. BA significantly inhibited the proliferation and migration of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) through targeting Skp2-SCF E3 ligase both in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, BA binding to Skp2, especially forming H-bonds with residue Lys145, decreases its stability by disrupting Skp1-Skp2 interactions, thereby inhibiting the Skp2-SCF E3 ligase and promoting the accumulation of its substrates; that is, E-cadherin and p27. In both subcutaneous and orthotopic xenografts, BA significantly inhibited the proliferation and metastasis of NSCLC through targeting Skp2-SCF E3 ligase and upregulating p27 and E-cadherin protein levels. Taken together, BA can be considered a valuable therapeutic candidate to inhibit metastasis of NSCLC.
Keywords: E-cadherin; NSCLC; Skp2; betulinic acid; metastasis.
© 2021 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394‐424. - PubMed
-
- Arbour KC, Riely GJ. Systemic therapy for locally advanced and metastatic non‐small cell lung cancer: a review. JAMA. 2019;322:764‐774. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2020KJ148/Project of south medicine innovation team in modern agricultural industry technology system of Guangdong Province
- 81802776/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82004161/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 201805010005/Guangzhou Science Technology and Innovation Commission Technology Research Projects
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

