Diethynyl Phosphinates for Cysteine-Selective Protein Labeling and Disulfide Rebridging
- PMID: 34080747
- PMCID: PMC8362001
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202100683
Diethynyl Phosphinates for Cysteine-Selective Protein Labeling and Disulfide Rebridging
Abstract
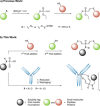
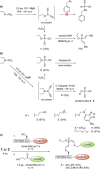
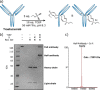
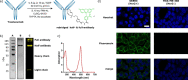
Diethynyl phosphinates were developed as bisfunctional electrophiles for the site-selective modification of peptides, proteins and antibodies. One of their electron-deficient triple bonds reacts selectively with a thiol and positions an electrophilic moiety for a subsequent intra- or intermolecular reaction with another thiol. The obtained conjugates were found to be stable in human plasma and in the presence of small thiols. We further demonstrate that this method is suitable for the generation of functional protein conjugates for intracellular delivery. Finally, this reagent class was used to generate functional homogeneously rebridged antibodies that remain specific for their target. Their modular synthesis, thiol selectivity and conjugate stability make diethynyl phosphinates ideal candidates for protein conjugation for biological and pharmaceutical applications.
Keywords: antibody rebridging; bioconjugation; cysteine-selective modification; phosphorous-based electrophiles; protein double-modification.
© 2021 The Authors. Angewandte Chemie International Edition published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The chemistry described in this manuscript is part of a patent application (Appl. Number: EP21170097.6).
Figures

Similar articles
-
DFT-Guided Discovery of Ethynyl-Triazolyl-Phosphinates as Modular Electrophiles for Chemoselective Cysteine Bioconjugation and Profiling.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022 Oct 10;61(41):e202205348. doi: 10.1002/anie.202205348. Epub 2022 Aug 22. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022. PMID: 35792701 Free PMC article.
-
The Nitrile Bis-Thiol Bioconjugation Reaction.J Am Chem Soc. 2024 Jan 10;146(1):274-280. doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c08762. Epub 2023 Dec 20. J Am Chem Soc. 2024. PMID: 38124442 Free PMC article.
-
oxSTEF Reagents Are Tunable and Versatile Electrophiles for Selective Disulfide-Rebridging of Native Proteins.Bioconjug Chem. 2023 Jun 21;34(6):994-1003. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.3c00005. Epub 2023 May 18. Bioconjug Chem. 2023. PMID: 37201197
-
Site-Selective Disulfide Modification of Proteins: Expanding Diversity beyond the Proteome.Chemistry. 2016 Nov 21;22(48):17112-17129. doi: 10.1002/chem.201602298. Epub 2016 Oct 25. Chemistry. 2016. PMID: 27778400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances of thiol-selective bioconjugation reactions.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2020 Oct;58:28-36. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2020.04.017. Epub 2020 Jul 7. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2020. PMID: 32645576 Review.
Cited by
-
Sensitive Immunofluorescent Detection of the PRAME Antigen Using a Practical Antibody Conjugation Approach.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 27;22(23):12845. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312845. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884647 Free PMC article.
-
Site-Specific Polymer-Protein-Polymer Conjugates for the Preparation of Dual Responsive Multilayer Nanoparticles.Small. 2025 Apr;21(14):e2500531. doi: 10.1002/smll.202500531. Epub 2025 Mar 4. Small. 2025. PMID: 40035613 Free PMC article.
-
Dual reactivity disulfide bridging reagents; enabling new approaches to antibody fragment bioconjugation.Chem Sci. 2022 Sep 27;13(39):11533-11539. doi: 10.1039/d2sc04531a. eCollection 2022 Oct 12. Chem Sci. 2022. PMID: 36320392 Free PMC article.
-
Chemoselective cysteine or disulfide modification via single atom substitution in chloromethyl acryl reagents.Chem Sci. 2021 Sep 9;12(40):13321-13330. doi: 10.1039/d1sc03250j. eCollection 2021 Oct 20. Chem Sci. 2021. PMID: 34777751 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide and Protein Cysteine Modification Enabled by Hydrosulfuration of Ynamide.ACS Cent Sci. 2024 Aug 21;10(9):1742-1754. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.4c01148. eCollection 2024 Sep 25. ACS Cent Sci. 2024. PMID: 39345815 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hoyt E. A., Cal P. M. S. D., Oliveira B. L., Bernardes G. J. L., Nat. Rev. Chem. 2019, 3, 147–171.
-
- Schumacher D., Hackenberger C. P. R., Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2014, 22, 62–69. - PubMed
-
- Gunnoo S. B., Madder A., ChemBioChem 2016, 17, 529–553. - PubMed
-
- Ochtrop P., Hackenberger C. P. R., Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2020, 58, 28–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

