The Clinical Decision Support System AMPEL for Laboratory Diagnostics: Implementation and Technical Evaluation
- PMID: 34081013
- PMCID: PMC8212627
- DOI: 10.2196/20407
The Clinical Decision Support System AMPEL for Laboratory Diagnostics: Implementation and Technical Evaluation
Abstract
Background: Laboratory results are of central importance for clinical decision making. The time span between availability and review of results by clinicians is crucial to patient care. Clinical decision support systems (CDSS) are computational tools that can identify critical values automatically and help decrease treatment delay.
Objective: With this work, we aimed to implement and evaluate a CDSS that supports health care professionals and improves patient safety. In addition to our experiences, we also describe its main components in a general manner to make it applicable to a wide range of medical institutions and to empower colleagues to implement a similar system in their facilities.
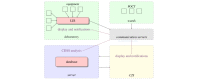
Methods: Technical requirements must be taken into account before implementing a CDSS that performs laboratory diagnostics (labCDSS). These can be planned within the functional components of a reactive software agent, a computational framework for such a CDSS.
Results: We present AMPEL (Analysis and Reporting System for the Improvement of Patient Safety through Real-Time Integration of Laboratory Findings), a labCDSS that notifies health care professionals if a life-threatening medical condition is detected. We developed and implemented AMPEL at a university hospital and regional hospitals in Germany (University of Leipzig Medical Center and the Muldental Clinics in Grimma and Wurzen). It currently runs 5 different algorithms in parallel: hypokalemia, hypercalcemia, hyponatremia, hyperlactatemia, and acute kidney injury.
Conclusions: AMPEL enables continuous surveillance of patients. The system is constantly being evaluated and extended and has the capacity for many more algorithms. We hope to encourage colleagues from other institutions to design and implement similar CDSS using the theory, specifications, and experiences described in this work.
Keywords: clinical decision support system (CDSS); computational architecture; digital health; laboratory medicine; reactive software agent.
©Maria Beatriz Walter Costa, Mark Wernsdorfer, Alexander Kehrer, Markus Voigt, Carina Cundius, Martin Federbusch, Felix Eckelt, Johannes Remmler, Maria Schmidt, Sarah Pehnke, Christiane Gärtner, Markus Wehner, Berend Isermann, Heike Richter, Jörg Telle, Thorsten Kaiser. Originally published in JMIR Medical Informatics (https://medinform.jmir.org), 03.06.2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: AMPEL is currently a public-funded research project and runs at ULMC and Muldental Clinics in Grimma and Wurzen. After completion of the project, it will be transferred to the controlling software Vismedica of Xantas AG to be commercialized. AK and JT from Xantas AG as well as all other co-authors declare that the future commercialization of AMPEL had no influence on the research or writing of the manuscript.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Improved patient safety through a clinical decision support system in laboratory medicine].Internist (Berl). 2020 May;61(5):452-459. doi: 10.1007/s00108-020-00775-3. Internist (Berl). 2020. PMID: 32221627 Review. German.
-
An interoperable clinical decision-support system for early detection of SIRS in pediatric intensive care using openEHR.Artif Intell Med. 2018 Jul;89:10-23. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2018.04.012. Epub 2018 May 9. Artif Intell Med. 2018. PMID: 29753616
-
Decision support systems in clinical practice: The case of venous thromboembolism prevention.Int J Risk Saf Med. 2015;27 Suppl 1:S104-5. doi: 10.3233/JRS-150709. Int J Risk Saf Med. 2015. PMID: 26639683
-
A hybrid hierarchical decision support system for cardiac surgical intensive care patients. Part II. Clinical implementation and evaluation.Artif Intell Med. 2009 Jan;45(1):53-62. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2008.11.010. Epub 2008 Dec 27. Artif Intell Med. 2009. PMID: 19112011
-
Clinical decision support systems in the pediatric intensive care unit.Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2009 Jan;10(1):23-8. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0b013e3181936b23. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2009. PMID: 19057443 Review.
Cited by
-
Refeeding Syndrome.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2023 Feb 17;120(7):107-114. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.m2022.0381. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2023. PMID: 36482748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development, Design and Utilization of a CDSS for Refeeding Syndrome in Real Life Inpatient Care-A Feasibility Study.Nutrients. 2023 Aug 24;15(17):3712. doi: 10.3390/nu15173712. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37686744 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Silveira DV, Marcolino MS, Machado EL, Ferreira CG, Alkmim MBM, Resende ES, Carvalho BC, Antunes AP, Ribeiro ALP. Development and Evaluation of a Mobile Decision Support System for Hypertension Management in the Primary Care Setting in Brazil: Mixed-Methods Field Study on Usability, Feasibility, and Utility. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2019 Mar 25;7(3):e9869. doi: 10.2196/mhealth.9869. https://mhealth.jmir.org/2019/3/e9869/ - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang J, Bao B, Shen P, Kong G, Yang Y, Sun X, Ding G, Gao B, Yang C, Zhao M, Lin H, Zhang L. Using electronic health record data to establish a chronic kidney disease surveillance system in China: protocol for the China Kidney Disease Network (CK-NET)-Yinzhou Study. BMJ Open. 2019 Aug 28;9(8):e030102. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-030102. https://bmjopen.bmj.com/lookup/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=31467053 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adnan M, Peterkin D, McLaughlin A, Hill N. HL7 Middleware Framework for Laboratory Notifications for Notifiable Diseases. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2015;214:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Courbis A, Murray RB, Arnavielhe S, Caimmi D, Bedbrook A, Van Eerd M, De Vries G, Dray G, Agache I, Morais-Almeida M, Bachert C, Bergmann KC, Bosnic-Anticevich S, Brozek J, Bucca C, Camargos P, Canonica GW, Carr W, Casale T, Fonseca JA, Haahtela T, Kalayci O, Klimek L, Kuna P, Kvedariene V, Larenas Linnemann D, Lieberman P, Mullol J, Ohehir R, Papadopoulos N, Price D, Ryan D, Samolinski B, Simons FE, Tomazic P, Triggiani M, Valiulis A, Valovirta E, Wagenmann M, Wickman M, Yorgancioglu A, Bousquet J. Electronic Clinical Decision Support System for allergic rhinitis management: MASK e-CDSS. Clin Exp Allergy. 2018 Dec 20;48(12):1640–1653. doi: 10.1111/cea.13230. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

