Diabetes and Cardiovascular Complications: The Epidemics Continue
- PMID: 34081211
- PMCID: PMC8173334
- DOI: 10.1007/s11886-021-01504-4
Diabetes and Cardiovascular Complications: The Epidemics Continue
Abstract
Purpose of review: The cardiovascular complications of type 1 and 2 diabetes are major causes of morbidity and mortality. Extensive efforts have been made to maximize glycemic control; this strategy reduces certain manifestations of cardiovascular complications. There are drawbacks, however, as intensive glycemic control does not impart perennial protective benefits, and these efforts are not without potential adverse sequelae, such as hypoglycemic events.
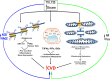
Recent findings: Here, the authors have focused on updates into key areas under study for mechanisms driving these cardiovascular disorders in diabetes, including roles for epigenetics and gene expression, interferon networks, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Updates on the cardioprotective roles of the new classes of hyperglycemia-targeting therapies, the sodium glucose transport protein 2 inhibitors and the agonists of the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor system, are reviewed. In summary, insights from ongoing research and the cardioprotective benefits of the newer type 2 diabetes therapies are providing novel areas for therapeutic opportunities in diabetes and CVD.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; Diabetes; Epigenetics; Interferon pathways; Mitochondrial dysfunction; Therapeutic agents.
Conflict of interest statement
Drs. Schmidt and Ramasamy report a patent US 9,353,3078 issued, a patent US 9,364,472 issued, a patent US 16/094270 pending, and a patent Europe 177,864,360.0 pending applications assigned to NYU Grossman School of Medicine. The other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation . IDF Diabetes Atlas. 9. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation; 2019. - PubMed
-
- International Diabetes Federation . Diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation; 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

