Evaluation of multi-component interventions for prevention of nosocomial pneumonia in older adults: a randomized, controlled trial
- PMID: 34081314
- PMCID: PMC8173511
- DOI: 10.1007/s41999-021-00506-3
Evaluation of multi-component interventions for prevention of nosocomial pneumonia in older adults: a randomized, controlled trial
Abstract
Aims: To evaluate the efficacy of multi-component interventions for prevention of hospital-acquired pneumonia in older patients hospitalized in geriatric wards.
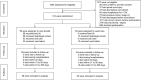
Methods: A randomized, parallel-group, controlled trial was undertaken in patients aged 65 and above who were admitted to a tertiary hospital geriatric unit from January 1, 2016 to June 30, 2018 for an acute non-respiratory illness. Participants were randomized by to receive either a multi-component intervention (consisting of reverse Trendelenburg position, dysphagia screening, oral care and vaccinations), or usual care. The outcome measures were the proportion of patients who developed hospital-acquired pneumonia during hospitalisation, and mean time from randomization to the next hospitalisation due to respiratory infections in 1 year.
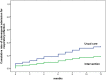
Results: A total of 123 participants (median age, 85; 43.1% male) were randomized, (n = 59) to intervention group and (n = 64) to control group. The multi-component interventions did not significantly reduce the incidence of hospital-acquired pneumonia but did increase the mean time to next hospitalisation due to respiratory infection (11.5 months vs. 9.5 months; P = 0.049), and reduced the risk of hospitalisation in 1 year (18.6% vs. 34.4%; P = 0.049). Implementation of multi-component interventions increased diagnoses of oropharyngeal dysphagia (35.6% vs. 20.3%; P < 0.001) and improved the influenza (54.5% vs 17.2%; P < 0.001) and pneumococcal vaccination rates (52.5% vs. 20.3%; P < 0.001).
Conclusions: The nosocomial pneumonia multi-component intervention did not significantly reduce the incidence of hospital-acquired pneumonia during hospitalisation but reduce subsequent hospitalisations for respiratory infections.
Clinical trial registration: ClinicalTrial.gov, NCT04347395.
Keywords: Multi-component interventions; Nosocomial infection; Older adults; Pneumonia; Randomized controlled trial.
© 2021. European Geriatric Medicine Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The main author attended a Pneumococcal Vaccine Expert Input forum in 2019 (an honorarium was received and donated to the Geriatric Department) and received sponsorship from Pfizer to attend an Asia Pneumococcal and Meningococcal Disease Conference in Hong Kong in 2016. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest, and this paper has not been published or presented elsewhere.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Safety and Efficacy of Imatinib for Hospitalized Adults with COVID-19: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Oct 28;21(1):897. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04819-9. Trials. 2020. PMID: 33115543 Free PMC article.
-
Testing the efficacy and safety of BIO101, for the prevention of respiratory deterioration, in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia (COVA study): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Jan 11;22(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04998-5. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33430924 Free PMC article.
-
Randomized clinical trial to evaluate safety and efficacy of convalescent plasma use among hospitalized patients with COVID-19 (PERUCONPLASMA): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2021 May 17;22(1):342. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05189-6. Trials. 2021. PMID: 34001174 Free PMC article.
-
Home Treatment of Older People with Symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection (COVID-19): A structured Summary of a Study Protocol for a Multi-Arm Multi-Stage (MAMS) Randomized Trial to Evaluate the Efficacy and Tolerability of Several Experimental Treatments to Reduce the Risk of Hospitalisation or Death in outpatients aged 65 years or older (COVERAGE trial).Trials. 2020 Oct 13;21(1):846. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04619-1. Trials. 2020. PMID: 33050924 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Reconvalescent plasma/camostat mesylate in early SARS-CoV-2 Q-PCR positive high-risk individuals (RES-Q-HR): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2021 May 17;22(1):343. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05181-0. Trials. 2021. PMID: 34001215 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Strategies to prevent ventilator-associated pneumonia, ventilator-associated events, and nonventilator hospital-acquired pneumonia in acute-care hospitals: 2022 Update.Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2022 Jun;43(6):687-713. doi: 10.1017/ice.2022.88. Epub 2022 May 20. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2022. PMID: 35589091 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased hospital-acquired respiratory infections among older inpatients during the COVID-19 pandemic: a retrospective observational study in a general hospital in China.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Sep 2;24(1):904. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09779-y. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39223461 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of the Hospital Frailty Risk Score in older adults hospitalized with community-acquired pneumonia.Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2024 Mar;24 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):135-141. doi: 10.1111/ggi.14697. Epub 2023 Oct 17. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2024. PMID: 37846810 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guidelines for the management of adults with hospital-acquired, ventilator-associated, and healthcare-associated pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;171:388–416. 10.1164/rccm.200405-644ST - PubMed
-
- Kalil AC, Metersky ML, Klompas M, Muscedere J, Sweeney DA, Palmer LB, et al. Management of adults with hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated pneumonia: 2016 Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the American Thoracic Society. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;63:e61–e111. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw353. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
