LUNAR :Drug Screening for Novel Coronavirus Based on Representation Learning Graph Convolutional Network
- PMID: 34081583
- PMCID: PMC8769035
- DOI: 10.1109/TCBB.2021.3085972
LUNAR :Drug Screening for Novel Coronavirus Based on Representation Learning Graph Convolutional Network
Abstract
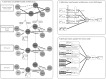
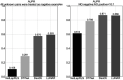
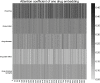
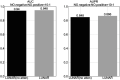
An outbreak of COVID-19 that began in late 2019 was caused by a novel coronavirus(SARS-CoV-2). It has become a global pandemic. As of June 9, 2020, it has infected nearly 7 million people and killed more than 400,000, but there is no specific drug. Therefore, there is an urgent need to find or develop more drugs to suppress the virus. Here, we propose a new nonlinear end-to-end model called LUNAR. It uses graph convolutional neural networks to automatically learn the neighborhood information of complex heterogeneous relational networks and combines the attention mechanism to reflect the importance of the sum of different types of neighborhood information to obtain the representation characteristics of each node. Finally, through the topology reconstruction process, the feature representations of drugs and targets are forcibly extracted to match the observed network as much as possible. Through this reconstruction process, we obtain the strength of the relationship between different nodes and predict drug candidates that may affect the treatment of COVID-19 based on the known targets of COVID-19. These selected candidate drugs can be used as a reference for experimental scientists and accelerate the speed of drug development. LUNAR can well integrate various topological structure information in heterogeneous networks, and skillfully combine attention mechanisms to reflect the importance of neighborhood information of different types of nodes, improving the interpretability of the model. The area under the curve(AUC) of the model is 0.949 and the accurate recall curve (AUPR) is 0.866 using 10-fold cross-validation. These two performance indexes show that the model has superior predictive performance. Besides, some of the drugs screened out by our model have appeared in some clinical studies to further illustrate the effectiveness of the model.
Figures
References
-
- Yang Y., et al. , “Epidemiological and clinical features of the 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak in China,” MedRxiv, 2020. - PubMed
-
- WHO. “Coronavirus disease (COVID-2019) situation reports,” Accessed: Jun. 9, 2020. [Online]. Available: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio.../
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

