Activated CD4+ T Cells and Highly Differentiated Alloreactive CD4+ T Cells Distinguish Operationally Tolerant Liver Transplantation Recipients
- PMID: 34081828
- PMCID: PMC9291234
- DOI: 10.1002/lt.26188
Activated CD4+ T Cells and Highly Differentiated Alloreactive CD4+ T Cells Distinguish Operationally Tolerant Liver Transplantation Recipients
Abstract
Spontaneous operational tolerance to the allograft develops in a proportion of liver transplantation (LT) recipients weaned off immunosuppressive (IS) drugs. Several studies have investigated whether peripheral blood circulating T cells could play a role in the development or identify operational tolerance, but never characterized alloreactive T cells in detail due to the lack of a marker for these T cells. In this study, we comprehensively investigated phenotypic and functional characteristics of alloreactive circulating T cell subsets in tolerant LT recipients (n = 15) using multiparameter flow cytometry and compared these with LT recipients on IS drugs (n = 23) and healthy individuals (n = 16). Activation-induced CD137 was used as a marker for alloreactive T cells upon allogenic stimulation. We found that central and effector memory CD4+ T cells were hyporesponsive against donor and third-party splenocyte stimulation in tolerant LT recipients, whereas an overall hyperresponsiveness was observed in alloreactive terminally differentiated effector memory CD4+ T cells. In addition, elevated percentages of circulating activated T helper cells were observed in these recipients. Lastly, tolerant and control LT recipients did not differ in donor-specific antibody formation. In conclusion, a combination of circulating hyperresponsive highly differentiated alloreactive CD4+ T cells and circulating activated T helper cells could discriminate tolerant recipients from a larger group of LT recipients.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Liver Transplantation published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures
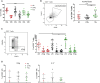
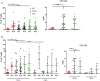
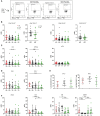



Comment in
-
Biomarkers of Operational Tolerance After Liver Transplantation: Are We There Yet?Liver Transpl. 2022 Jan;28(1):15-16. doi: 10.1002/lt.26270. Epub 2021 Sep 7. Liver Transpl. 2022. PMID: 34407265 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ojo AO, Held PJ, Port FK, Wolfe RA, Leichtman AB, Young EW, et al. Chronic renal failure after transplantation of a nonrenal organ. N Engl J Med 2003;349:931‐940. - PubMed
-
- Duizendstra AA, de Knegt RJ, Betjes MGH, Coenen S, Murad SD, de Man RA, et al. Immunosuppressive drug withdrawal late after liver transplantation improves the lipid profile and reduces infections. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019;31:1444‐1451. - PubMed
-
- Orlando G, Soker S, Wood K. Operational tolerance after liver transplantation. J Hepatol 2009;50:1247‐1257. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

