Comparison of Roche and Lumipulse quantitative SARS-CoV-2 antigen test performance using automated systems for the diagnosis of COVID-19
- PMID: 34082089
- PMCID: PMC8166457
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2021.05.067
Comparison of Roche and Lumipulse quantitative SARS-CoV-2 antigen test performance using automated systems for the diagnosis of COVID-19
Abstract
Background: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) continues to spread worldwide. Here, we evaluated the performance of two quantitative antigen (Ag) tests, the Roche and Lumipulse Ag tests, using automated platforms.
Methods: We collected 637 nasopharyngeal swab samples from 274 individuals. Samples were subjected to quantitative reverse transcription PCR (RT-qPCR), the Roche Ag test and Lumipulse Ag test.
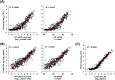
Results: When RT-qPCR was used as a reference, the overall concordance rate of the Roche Ag test was 77.1% (491/637) with 70.0% (341/487) sensitivity and 100% specificity (150/150). When inconclusive results of the Lumipulse Ag test were excluded, the overall concordance rate of the Lumipulse Ag test was 88.3% (467/529) with 84.8% (330/389) sensitivity and 97.9% (137/140) specificity. The overall concordance rate between the Roche and Lumipulse Ag tests was 97.9% (518/529) with 96.7% (322/333) sensitivity and 100% (196/196) specificity. Quantitative Ag levels determined using the Roche and Lumipulse Ag tests were highly correlated (R2 = 0.922). The Roche and Lumipulse Ag tests showed high concordance up to nine days after symptom onset, with progressively lower concordance after that.
Conclusions: The Roche and Lumipulse Ag tests showed equivalent assay performance and represent promising approaches for diagnosing coronavirus disease 2019.
Keywords: Antigen; COVID-19; Lumipulse; Roche; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control . 2020. Rapid increase of a SARS-CoV-2 variant with multiple spike protein mutations observed in the United Kingdom; pp. 1–13.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

