A Bibliometric and Mapping Analysis of Glaucoma Research between 1900 and 2019
- PMID: 34082178
- PMCID: PMC9438508
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ogla.2021.05.008
A Bibliometric and Mapping Analysis of Glaucoma Research between 1900 and 2019
Abstract
Purpose: To explore the relevance of scientific production on glaucoma using bibliometric tools.
Design: Bibliographic study.
Participants: Original articles published from 1900 through 2019.
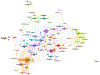
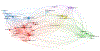
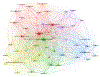
Methods: We performed a search in Web of Science for documents published between 1900 and 2019. We used bibliometric indicators to explore documents production, dispersion, distribution, time of duplication, and annual growth, as characterized by Price's law of scientific literature growth, Lotka's law, the transient index, and the Bradford model. We also calculated the participation index of different countries and institutions. Finally, we explored with bibliometric mapping the co-occurrence networks for the most frequently used terms in glaucoma research.
Main outcome measures: Bibliometric indicators for individuals, institutions, and countries.
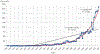
Results: A total of 33 631 original articles were collected from the timeframe 1900 through 2019. Price's law showed an exponential growth. Scientific production was adjusted better to exponential growth (r = 0.967) than linear growth (r = 0.755). Literature on glaucoma research increased its growth in the last 30 years at a rate of 5.1% per year with a production that doubled its size every 13.9 years. The transience index was 60.08%; this indicates that most of the scientific production is the output of very few authors. Bradford's law showed a high concentration of articles published in a small core of specialized journals. Lotka's law indicated that the distribution of authors is concentrated heavily in small producers. The United States and University of London demonstrated the highest production of original articles. Map network visualization showed the generated term map detailing clusters of closely related terms.
Conclusions: Glaucoma literature has grown exponentially. A very high rate of transience was found that indicates the presence of numerous authors who sporadically publish on this topic. No evidence of a saturation point in the glaucoma literature was observed.
Keywords: Bibliometric indicators; Bibliometric mapping; Collaborative networks; Glaucoma; Scientific production.
Copyright © 2021 American Academy of Ophthalmology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bibliometric study of scientific research on optometric visual therapy.J Optom. 2020 Jul-Sep;13(3):191-197. doi: 10.1016/j.optom.2019.12.007. Epub 2020 May 30. J Optom. 2020. PMID: 32487462 Free PMC article.
-
Multifocal contact lenses: A bibliometric study.J Optom. 2022 Jan-Mar;15(1):53-59. doi: 10.1016/j.optom.2020.07.007. Epub 2020 Sep 7. J Optom. 2022. PMID: 32907788 Free PMC article.
-
[Bibliometric evaluation of the Spanish scientific output in neurosciences. Analysis of the publication with international readership between 1984 and 1993].Rev Neurol. 1996 Apr;24(128):417-26. Rev Neurol. 1996. PMID: 8721919 Spanish.
-
Trends in the scientific literature on atypical antipsychotic drugs in the United Kingdom: a bibliometric study.Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2019 Feb 14;9:2045125318820207. doi: 10.1177/2045125318820207. eCollection 2019. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30800284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mapping the scientific research on atypical antipsychotic drugs in Spain: a bibliometric assessment.Actas Esp Psiquiatr. 2013 Nov-Dec;41(6):349-60. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Actas Esp Psiquiatr. 2013. PMID: 24203507 Review.
Cited by
-
Depicting Developing Trend and Core Knowledge of Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma: A Bibliometric and Visualized Analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 5;9:922527. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.922527. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35865166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research hotspots and trends of microRNAs in intervertebral disc degeneration: a comprehensive bibliometric analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2023 Apr 15;18(1):302. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-03788-4. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 37061725 Free PMC article.
-
Insight into the characteristics of research published in traditional, complementary, alternative, and integrative medicine journals: a bibliometric analysis.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021 Jul 1;21(1):185. doi: 10.1186/s12906-021-03354-7. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021. PMID: 34210316 Free PMC article.
-
Latest research hot spots of glaucoma management using selective laser trabeculoplasty: a bibliometric analysis and visualized review.Int Ophthalmol. 2025 Aug 22;45(1):346. doi: 10.1007/s10792-025-03699-9. Int Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40844630 Review.
-
Bibliometric analysis of the uveitis literature and research trends over the past two decades.BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2023 Sep;8(1):e001330. doi: 10.1136/bmjophth-2023-001330. BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37714667 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tham YC, Li X, Wong TY, et al. Global prevalence of glaucoma and projections of glaucoma burden through 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology. 2014;121:2081–2090. - PubMed
-
- Weinreb RN, Leung CK, Crowston JG, et al. Primary open-angle glaucoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16067. - PubMed
-
- Johnson CA, Sample PA, Cioffi GA, et al. Structure and function evaluation (SAFE): I. Criteria for glaucomatous visual field loss using standard automated perimetry (SAP) and short wavelength automated perimetry (SWAP). Am J Ophthalmol. 2002;134:177–185. - PubMed

