MLN4924 inhibits cell proliferation by targeting the activated neddylation pathway in endometrial carcinoma
- PMID: 34082605
- PMCID: PMC8182194
- DOI: 10.1177/03000605211018592
MLN4924 inhibits cell proliferation by targeting the activated neddylation pathway in endometrial carcinoma
Abstract
Objective: To explore the neddylation pathway, found to be highly activated in various cancers, as a potential therapeutic target in endometrial carcinoma, one of the three most frequent malignant tumours in the female reproductive system.
Methods: Data from The Cancer Genome Atlas were analysed using online servers. Expression levels of key neddylation genes were validated by reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction and western blots of tumour and adjacent tissues. Underlying mechanisms and the effects on cell activities of the neddylation pathway-specific inhibitor, MLN4924, were investigated in endometrial cancer cell lines.
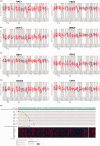
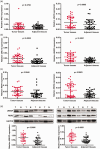
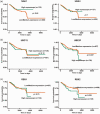
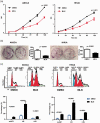
Results: Key neddylation enzymes, ubiquitin conjugating enzyme E2 M (UBC12), ubiquitin conjugating enzyme E2 F (UBE2F), ring-box 1 (RBX1) and ring finger protein 7 (RBX2), were significantly overexpressed in endometrial carcinoma tissues versus normal tissues, but only UBE2F and RBX2 positively correlated with patient survival. MLN4924 significantly suppressed proliferation and colony formation in EC cells by inducing DNA re-replication, cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Mechanism study revealed that MLN4924 induced the accumulation of cullin-RING ligase substrates in vitro.
Conclusions: The neddylation pathway was identified to play an important role in endometrial cancer. The neddylation specific inhibitor, MLN4924, may be a potential therapeutic drug for endometrial carcinoma.
Keywords: Endometrial cancer; MLN4924; apoptosis; cell cycle arrest; cullin-RING ligase; neddylation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Validation of NEDD8-conjugating enzyme UBC12 as a new therapeutic target in lung cancer.EBioMedicine. 2019 Jul;45:81-91. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.06.005. Epub 2019 Jun 14. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 31208947 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of glioblastoma by targeting the overactivated protein neddylation pathway.Neuro Oncol. 2015 Oct;17(10):1333-43. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nov066. Epub 2015 Apr 22. Neuro Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25904638 Free PMC article.
-
Overactivated neddylation pathway as a therapeutic target in lung cancer.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014 May 22;106(6):dju083. doi: 10.1093/jnci/dju083. Print 2014 Jun. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014. PMID: 24853380
-
Targeting Neddylation pathways to inactivate cullin-RING ligases for anticancer therapy.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014 Dec 10;21(17):2383-400. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5795. Epub 2014 Feb 20. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014. PMID: 24410571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Double-Edged Effects of MLN4924: Rethinking Anti-Cancer Drugs Targeting the Neddylation Pathway.Biomolecules. 2024 Jun 21;14(7):738. doi: 10.3390/biom14070738. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39062453 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated analysis reveals the regulatory mechanism of the neddylation inhibitor MLN4924 on the metabolic dysregulation in rabbit granulosa cells.BMC Genomics. 2024 Mar 6;25(1):254. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10118-3. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38448814 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of NEDD8 NEDDylation induced apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells via p53 signaling pathway.Biosci Rep. 2022 Aug 31;42(8):BSR20220994. doi: 10.1042/BSR20220994. Biosci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35880551 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in colorectal cancer research: Unveiling the cellular and molecular mechanisms of neddylation (Review).Int J Oncol. 2024 Apr;64(4):39. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2024.5627. Epub 2024 Feb 23. Int J Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38391033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein Stability Regulation in Osteosarcoma: The Ubiquitin-like Modifications and Glycosylation as Mediators of Tumor Growth and as Targets for Therapy.Cells. 2024 Mar 18;13(6):537. doi: 10.3390/cells13060537. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38534381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The E3 Ligases in Cervical Cancer and Endometrial Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 30;14(21):5354. doi: 10.3390/cancers14215354. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358773 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li BL, Lu W, Qu JJ, et al.. Loss of exosomal miR-148b from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes endometrial cancer cell invasion and cancer metastasis. J Cell Physiol 2019; 234: 2943–2953. - PubMed
-
- Morice P, Leary A, Creutzberg C, et al.. Endometrial cancer. Lancet 2016; 387: 1094–1108. - PubMed
-
- Fleming GF, Brunetto VL, Cella D, et al.. Phase III trial of doxorubicin plus cisplatin with or without paclitaxel plus filgrastim in advanced endometrial carcinoma: a Gynecologic Oncology Group Study. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 2159–2166. - PubMed
-
- Rabinovich A. Neo-adjuvant chemotherapy for advanced stage endometrial carcinoma: a glimmer of hope in select patients. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2016; 293: 47–53. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

