Cost utility of fractional exhaled nitric oxide monitoring for the management of children asthma
- PMID: 34082766
- PMCID: PMC8173882
- DOI: 10.1186/s12962-021-00287-3
Cost utility of fractional exhaled nitric oxide monitoring for the management of children asthma
Abstract
Introduction: Fractional exhaled nitric oxide is a simple, non-invasive measurement of airway inflammation with minimal discomfort to the patient and with results available within a few minutes. This study aimed to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of asthma management using fractional exhaled nitric oxide monitoring in patients between 4 and 18 years of age.
Methods: A Markov model was used to estimate the cost-utility of asthma management using fractional exhaled nitric oxide monitoring versus asthma management without using fractional exhaled nitric oxide monitoring (standard therapy) in patients between 4 and 18 years of age. Cost data were obtained from a retrospective study on asthma from a tertiary center, in Medellin, Colombia, while probabilities of the Markov model and utilities were obtained from the systematic review of published randomized clinical trials. The analysis was carried out from a societal perspective.
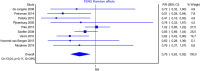
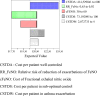
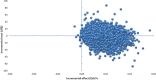
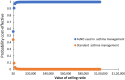
Results: The model showed that fractional exhaled nitric oxide monitoring was associated with a lower total cost than standard therapy (US $1333 vs. US $1452 average cost per patient) and higher QALYs (0.93 vs. 0.92 average per patient). The probability that fractional exhaled nitric oxide monitoring provides a more cost-effective use of resources compared with standard therapy exceeds 99% for all willingness-to-pay thresholds.
Conclusion: Asthma management using fractional exhaled nitric oxide monitoring was cost-effective for treating patients between 4 and 18 years of age with mild to moderate allergic asthma. Our study suggests evidence that could be used by decision-makers to improve clinical practice guidelines, but this should be replicated in different clinical settings.
Keywords: Health economics; Healthcare; Public health.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest in this publication.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fractional exhaled nitric oxide and eosinophil count in induced sputum to guide the management of children with asthma: a cost-utility analysis.BMC Pulm Med. 2022 Jun 28;22(1):257. doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-02027-6. BMC Pulm Med. 2022. PMID: 35765011 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the Budget Impact of Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide Monitoring in the Management of Childhood Asthma: The Colombian National Health System Perspective.J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2022 Jun 20;32(3):200-205. doi: 10.18176/jiaci.0690. Epub 2021 Apr 13. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2022. PMID: 33847566
-
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Monitoring Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide (FeNO) in the Management of Asthma.Manag Care. 2018 Jul;27(7):42-48. Manag Care. 2018. PMID: 29989901
-
A Review of the Utility and Cost Effectiveness of Monitoring Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide (FeNO) in Asthma Management.Manag Care. 2018 Jul;27(7):34-41. Manag Care. 2018. PMID: 29989900 Review.
-
Nitric oxide in allergic airway inflammation.Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003 Apr;3(2):133-7. doi: 10.1097/00130832-200304000-00007. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12750610 Review.
Cited by
-
Fractional exhaled nitric oxide and eosinophil count in induced sputum to guide the management of children with asthma: a cost-utility analysis.BMC Pulm Med. 2022 Jun 28;22(1):257. doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-02027-6. BMC Pulm Med. 2022. PMID: 35765011 Free PMC article.
-
Can the Chinese study on the normal range of FeNO in children evaluate standardized asthma treatment efficacy in 6- to 12-year-old children?Front Pediatr. 2023 Sep 19;11:1189496. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1189496. eCollection 2023. Front Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37794961 Free PMC article.
-
Association of fractional exhaled nitric oxide with asthma morbidity in urban minority children.J Asthma. 2023 Mar;60(3):553-564. doi: 10.1080/02770903.2022.2073549. Epub 2022 May 15. J Asthma. 2023. PMID: 35499408 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Fraction Exhaled Nitric Oxide (FeNO) in asthma management: an Italian consensus statement on clinical and economic aspects.Multidiscip Respir Med. 2025 Apr 8;20(1):1006. doi: 10.5826/mrm.2025.1006. Multidiscip Respir Med. 2025. PMID: 40197695 Free PMC article.
-
Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide Testing for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma: a Health Technology Assessment.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2024 Jul 31;24(5):1-225. eCollection 2024. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2024. PMID: 39329005 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global Iniciative for Asthma Management and Prevention 2020. www.ginaasthma.org.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources