CC and CXC chemokines play key roles in the development of polyomaviruses related pathological conditions
- PMID: 34082771
- PMCID: PMC8173740
- DOI: 10.1186/s12985-021-01582-4
CC and CXC chemokines play key roles in the development of polyomaviruses related pathological conditions
Abstract
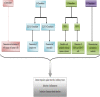
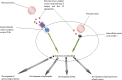
It has been reported that polyomaviruses are the microbes which can be a cause of several human pathological conditions including cancers, nephropathy, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and gynaecological disease. Although investigators proposed some mechanisms used by the viruses to induce the disorders, the roles played by chemokines in the pathogenesis of polyomaviruses infections are yet to be clarified. This review article investigated recent studies regarding the roles played by chemokines in the pathogenesis of the polyomaviruses infections. The research in the literature revealed that CXC chemokines, including CXCL1, CXCL5, CXCL8, CXCL9, CXCL10, CXCL11, CXCL12 and CXCL16, significantly participate in the pathogenesis of polyomaviruses. CC chemokines, such as CCL2, CCL5 and CCL20 also participate in the induction of the pathological conditions. Therefore, it appears that CXC chemokines may be considered as the strategic factors involved in the pathogenesis of polyomaviruses.
Keywords: CC chemokines; CXC chemokines; Cancer; Nephropathy; Polyomaviruses.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no competing interest to declare.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

