VEGFR1-tyrosine kinase signaling in pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 34082837
- PMCID: PMC8173728
- DOI: 10.1186/s41232-021-00166-7
VEGFR1-tyrosine kinase signaling in pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is not only an important factor for angiogenesis but also lung development and homeostasis. VEGF-A binds three tyrosine kinase (TK) receptors VEGFR1-3. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is one of the poor prognoses of lung diseases. The relationship of VEGF and IPF remains to be clarified. Treatment with nintedanib used for the treatment of IPF reduced fibroblast proliferation, inhibited TK receptors, platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR), fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR), and VEGFR. Because the effect of that treatment is still not satisfactory, the emergence of new therapeutic agents is needed. This review describes the enhancement of pulmonary fibrosis by VEGFR1-TK signal and suggests that the blocking of the VEGFR1-TK signal may be useful for the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis.
Keywords: CXCR4; Pulmonary fibrosis; SDF-1; VEGFR1+ cells; VEGFR1-TK.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
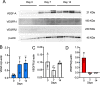

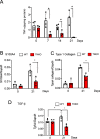

References
-
- Oishi Y, Manabe I. Macrophages in inflammation, repair and regeneration. Int Immunol. 2018;30:511–529. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

